What is LoRa and LoRaWAN network?
LoRa network is one of the low-power WAN communication technologies and is a proprietary Semtech technology for ultra-long-range wireless transmission based on spread spectrum technology.
LoRaWAN network is a set of communication protocols and system architecture designed for LoRa long-range communication networks. It is a Media Access Control (MAC) layer protocol.
Companies investing in digital transformation and IoT can use a reliable, low-cost private wireless network that can manage hundreds of low-power devices over a wide range.
Thanks to its wide coverage, use of unlicensed spectrum, and reduced power consumption (compared to Wi-Fi and Bluetooth), the dedicated LoRa network is ideally suited to connect with smart sensors and other low-power devices and can send data over long distances.

LoRaWAN network operates using unlicensed sub-gigahertz spectrum
One of the key considerations when planning a dedicated wireless network may be the use of licensed or unlicensed channels. While some of the new LTE NB-IoT products can operate on unlicensed bands, most cellular devices operate on licensed spectrum.
WiFi and Bluetooth use unlicensed spectrum in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. Despite this, those frequencies are still so crowded that they pose serious reliability problems, and the range of gateways is limited to a few meters.
LoRaWAN networks use unlicensed sub-gigahertz radio bands, such as 169 MHz, 433 MHz, 868 MHz (Europe), and 915 MHz (North America). The lower frequency bands allow data rates from 0.3 kbps to 50 kbps.
In addition, the use of the sub-gigahertz band allows for remote connectivity up to 10 km (6 miles) from the device.
One of the biggest advantages of the LoRaWAN network is that, unlike cellular telephony, it can operate in an unlicensed spectrum. Fees and costs and private network deployments are much cheaper. Therefore, with the LoRaWAN network, you can set up private networks.
LoRaWAN network offers strong encryption and reliability
LoRaWAN-connected devices and gateways to the LoRa network can protect data traffic using AES encryption. In addition, network security ensures the authenticity of the nodes in the network and the secure application layer ensures that user application data remains local even when the network is connected to the cloud.
Wireless communication takes advantage of the remote nature of the LoRa physical layer, allowing for single-hop links between end devices and one or more gateways. The use of the sub-gigahertz band provides a remote connection that can reach devices up to 10 km (6 miles) away.
In addition, the LoRa physical layer supports multicast addressing groups to perform tasks such as firmware over-the-air (FOTA) upgrades.
LoRaWAN network is suitable for large areas such as smart buildings, factories, and airports
The latest example of a private LoRaWAN network implementation is the new network at Schiphol Airport in Amsterdam.
The network covers all public areas such as arrival and departure halls, lounges, docks, and Schiphol Plaza, as well as non-public areas such as the baggage basement and aprons.
The LoRaWAN-based network infrastructure and solution deploys a network of sensors, including accelerometers, barometers, and magnetometers, all of which transmit and monitor data such as room temperature and humidity levels. There is even data from more than 500 sensors that are used to assess the cleanliness of the toilets.
Furthermore, according to the press release, the Schiphol LoRaWAN network enables global orchestration. It accelerates the digitization of airports and provides new services for operations, guest and passenger handling as well as shops, restaurants, and hotels.
Easy to scale from private to public LoRaWAN network
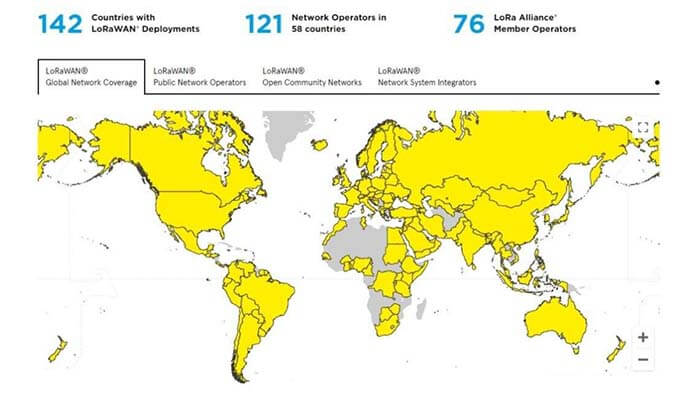
Public LoRaWAN network services can provide connectivity when external devices that are not within the range of a private network need to be connected, without having to invest in additional equipment. In this way, organizations can maintain a simple, unified IoT infrastructure.
Instead, one can start using an existing LoRaWAN public network and then connect a local dedicated gateway.
According to the LoRa Alliance, there are more than 120 public LoRaWAN networks operating in more than 145 countries/regions worldwide. Many of the public networks are operated by operators who charge usage fees. There are also many open community networks that provide LoRa connectivity to local organizations.
The LORA Consortium sees private networks as one of the trends for 2022, another major development in IoT that will continue the huge growth in private industrial LoRaWAN deployments.
Besides the What is the LoRaWAN Network Spectrum article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
4G vs 5G: What is the difference between 4G and 5G?
How to Choose the Best Antenna for Lora?
