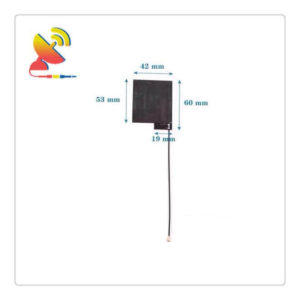
NFC Antennas
-
Small RFID Antenna NFC 13.56 MHz Antenna
Read more -
Small NFC Antenna Flexible PCB Antenna
Read more -
NFC Tag Antenna 13.56 MHz Antenna Design
Read more -
NFC Reader Antenna 13.56 MHz Flex PCB Antenna
Read more -
NFC Loop Antenna 13.56 MHz NFC Coil Design
Read more -
NFC Long Range Antenna Flexible Antenna
Read more -
NFC Flex PCB Antenna 13.56 MHz Antenna
Read more -
NFC Flex Antenna 13.56 MHz Antenna
Read more -
NFC Coil Antenna 13.56 MHz RFID Antenna Design
Read more -
NFC 13.56 Antenna Wireless RFID Antenna
Read more -
Near Field RFID 13.56 MHz Antenna
Read more -
Near Field Communication Antenna 13.56 MHz Antenna
Read more -
Long Range NFC Antenna Flex PCB Antenna
Read more -
High-performance RFID 13.56 MHz NFC PCB Antenna
Read more -
High Gain RFID Antenna 13.56 MHz Flexible Antenna
Read more -
High gain RFID Antenna 13.56 MHz Antenna
Read more -
Flexible NFC Antenna 13.56 MHz RFID Antenna
Read more -
Flexible Antenna NFC 13.56 MHz Antenna
Read more -
13.56MHz Antenna NFC PCB Antenna
Read more -
13.56 MHz RFID PCB Antenna NFC Antenna
Read more -
13.56 MHz RFID Chip Antenna Ipex Antenna
Read more -
13.56 MHz RFID Antenna Ipex Antenna
Read more -
13.56 MHz NFC Chip Antenna Flexible Antenna
Read more -
13.56 MHz NFC Antenna Tuning Flexible Antenna
Read more -
13.56 MHz NFC Antenna PCB trace Antenna
Read more -
13.56 MHz NFC Antenna Design
Read more -
13.56 MHz Long Range Antenna Ipex Antenna
Read more -
13.56 MHz Flexible PCB NFC Antenna
Read more
NFC Antennas Manufacturer
C&T RF Antennas Inc is the NFC Antennas manufacturer in China.
What is Near Field Communication(NFC)?
Near Field Communication (NFC) is an emerging technology that allows devices using NFC technology (e.g. cell phones) to exchange data in close proximity to each other.
Near Field Communication is evolved from the integration of contactless radio frequency identification (RFID) and interconnection and interoperability technology.
By integrating the functions of the inductive reader, inductive card, and peer-to-peer communication on a single chip, mobile terminals are used to realize mobile payment, electronic ticketing, access control, mobile identification, anti-counterfeiting, and other applications.
NFC is based on contactless radio frequency identification (RFID) technology, combined with wireless interconnection technology developed, which provides a very safe and fast communication method for various electronic products that are becoming more and more popular in our daily life.
NFC’s “near field” refers to the proximity of electromagnetic field radio waves. Because radio waves are actually electromagnetic waves, they follow Maxwell’s equations.
The electric field and the magnetic field in the process of propagation from the transmitting antenna to the receiving antenna will always alternate energy conversion, and enhance each other in the conversion, for example, the radio signal used in our cell phones is using this principle to propagate, this method is called far-field communication.
Within 10 wavelengths of electromagnetic waves, the electric and magnetic fields are independent of each other, when the electric field has little meaning, but the magnetic field can be used for short-range communication, which we call near-field communication.
Near-field communication service combines near-field communication technology and mobile communication technology to realize various functions such as electronic payment, identity authentication, ticketing, data exchange, anti-counterfeiting, advertising, etc.
It is a new type of service in the field of mobile communication. Near-field communication service enhances the function of cell phones, makes the user’s consumption behavior gradually go electronic, and establishes a new type of user consumption and business model.
The application of NFC technology has received widespread attention worldwide, and different players such as telecom operators and cell phone manufacturers at home and abroad have carried out pilot applications, and some international associations are actively working on standardization.
According to the prediction of relevant organizations in the industry, cell phone applications based on near-field communication technology will become the next killer application for mobile value-added services.
What is the source of near-field communication(NFC) technology?
According to the relevant information, in 2003, Sony (sony) company and the then Philipssemiconductor (now NXP NXP Semiconductors) cooperate, with plans based on contactless radio frequency card technology to develop a more secure and fast, and compatible with wireless communication technology.
After several months of research and development, the two sides jointly released a wireless communication technology compatible with the IS014443 contactless card protocol, named NFC (Near Field Communication), the specific communication specification called NFCIP-1 specification.
Not long after the release of the NFC technology, the two parties submitted a draft standard to the European Computer Manufacturers Association (ECMA) to become a standard for near-field communication and was soon recognized as the ECMA.340 standard, followed by a standard application to ISO/ IEC with the help of ECMA and was finally recognized as the ISO/IECl8092 standard.
What is the standard for near-field communication/NFC technology?
Near Field Communication (NFC) technology is a standard developed by Nokia, Philips, and Sony, and is standardized under ISO 18092, ECMA 340, and ETSI TS 102 190, and is also compatible with the widely used ISO 14443, Type-A, ISO 15693, B and B standards. Felica standard contactless smart card infrastructure.
It was audited by the ISO/IEC (International Organization for Standardization/International Electrotechnical Commission) on December 8, 2003, and became an international standard on March 18, 2004. ECMA (European Computer Manufacturers Association) recognized as a
The European standard on March 18, 2004, the adopted standards are listed as ISO/IEC 18092 (NFCIP-1), ECMA-340, ECMA-352, ECMA-356, ECMA-362, ISO/IEC 21481 (NFCIP-2).
Near-field communication standards detail the modulation scheme, coding, transmission speed, and frame format of the RF interface for near-field communication devices, as well as the initialization scheme and conditions required for data conflict control during the initialization of active and passive near-field communication modes, in addition to defining the transmission protocol, including protocol initiation and data exchange methods.
How does near-field communication/NFC technology work?
NFC is a short-range, high-frequency radio technology. The NFCIP-1 standard specifies that the communication distance of NFC is within 10 cm, the operating frequency is 13.56 MHz, and the transmission speed is 106 Kbit/s, 212 Kbit/s, or 424 Kbit/s.
The NFCIP-1 standard specifies in detail the transmission speed, codec method, modulation scheme, and frame format of the RF interface for NFC devices, and this standard also defines the transmission protocol of NFC, which includes the initiation protocol and data exchange method, etc.
NFC working modes are divided into passive and active modes. In the passive mode, the NFC initiating device (also called the master device) requires a power supply device, and the master device uses the energy of the power supply device to provide the RF field and send the data to the NFC target device (also called the slave device) at one of the transmission rates of 106kbps, 212kbps, or 424kbps.
The slave device does not generate an RF field, so it can not need power supply equipment, but use the RF field generated by the master device to convert to electrical power for the circuitry of the slave device, receive the data sent by the master device, and use the load modulation (load modulation) technology to transfer the data from the slave device back to the master device at the same speed.
This mode of operation is called passive mode because the slave device does not generate RF fields, but passively receives RF fields generated by the master device.
In this mode, the NFC master device can detect contactless cards or NFC target devices and establish a connection with them.
Inactive mode, both the initiating device and the target device must actively generate RF fields when sending data to each other, so it is called active mode, and they both need power supply devices to provide the energy to generate RF fields.
This communication mode is the standard model for peer-to-peer network communication and allows for very fast connection rates.
What are the main forms of application of near-field communication technology?
The NFC standard specifies a flexible gateway system for compatibility with contactless smart cards in three operating modes: point-to-point communication mode, reader mode, and NFC card emulation mode.
Point-to-point mode
Point-to-point mode, two NFC devices in this mode can exchange data. For example, multiple NFC-enabled digital cameras and cell phones can use NFC technology to wirelessly interconnect with each other to exchange data such as virtual business cards or digital photos.
For the peer-to-peer format, the key is to connect two NFC-enabled devices so that data transfer between the points is possible.
After taking the peer-to-peer form as the premise, the NFC-enabled cell phone and the computer, and other related devices can truly achieve peer-to-peer wireless connection and data transmission, and in the subsequent related applications, not only for local applications but also for network applications.
Therefore, the application of point-to-point form, for the rapid Bluetooth connection between different devices, and its communication data transmission has a very important role.
Reader mode
In read/write mode, this mode NFC devices are used as contactless readers and writers. For example, NFC-enabled cell phones play the role of reader/writer when interacting with tags, and NFC-enabled cell phones can read and write tags that support the NFC data format standard.
NFC communication in reader mode is used as a contactless reader to read relevant information from exhibition information electronic tags, movie posters, advertising pages, etc.
Card reader mode NFC cell phone can collect data resources from TAG and complete information processing functions according to certain application requirements, some application functions can be completed directly locally, and some need to combine with TD-LTE and other mobile communication networks to complete.
NFC application areas based on card reader mode include advertisement reading, ticket reading, cinema ticket sales, etc. For example, if a movie poster has a TAG tag attached to the back, the user can carry a cell phone supporting NFC protocol to obtain movie information and also connect to buy movie tickets.
Card reader NFC mode can also support bus stop information, tourist attractions map information access, and improve the convenience of people travel traffic.
Card simulation form
Simulation card mode, this mode is to simulate the device with NFC function as a tag or non-contact card, for example, an NFC-enabled cell phone can be read as an access card, bank card, etc.
The key to the card emulation mode is to emulate the NFC-enabled device into a contactless card mode, e.g., a bank card with an access card, etc. For example, bank cards and access cards.
This form of key application in shopping malls or transportation and other non-contact mobile payment, in the specific application process, the user only needs to their cell phones or other relevant electronic devices close to the card reader, while entering the corresponding password can make the transaction.
For the card in the form of card simulation, the key is to implement the power supply process through the RF domain with the non-contact reader, so that even if the NFC device has no power, it can also continue to work.
In addition, for the application of the card simulation form, data can be collected in the NFC-enabled device and transmitted to the corresponding processing system for processing, and this form can also be applied to various aspects such as prohibition systems and local payments.
What are the characteristics of near-field communication technology?
Near-field communication is a near-field wireless communication technology developed based on RFID technology.
Like RFID, near-field communication information is also transmitted by means of electromagnetic induction coupling in the radio frequency part of the spectrum, but there is still a big difference between the two.
The transmission range of near-field communication is smaller than that of RFID, which can reach 0~1m, but due to the unique signal attenuation technology adopted by near-field communication, near-field communication has low cost, high bandwidth, and low energy consumption compared to RFID.
The main features of near-field communication technology are as follows.
(1) Wireless communication technology used for close range (within 10cm) secure communication.
(2) RF frequency: 13.56MHz.
(3) RF compatibility: ISO 14443, ISO 15693, Felica standard.
(4) Data transmission speed: 106 kbit/s, 212 kbit/s, 424 kbit/s.
Comparison of NFC and other technologies
Current proximity wireless communication technologies include RFID, Bluetooth, infrared, etc. NFC is a short-range, high-frequency wireless communication technology that allows contactless point-to-point data transmission between electronic devices.
Its operating frequency is 13.56MHz, the communication distance is 0~20cm (most products are actually within 10cm), and the transmission rate can be 106kbit/s, 212kbit/s, 424 kbit/s, and 848kbit/s.
In addition to NFC, proximity wireless communication technologies mainly include radio frequency identification (RFID), Bluetooth (Bluetooth), ZigBee, infrared, Wi-Fi, and other technologies.
NFC and RFID comparison
First, the mode of operation is different. NFC is a point-to-point communication function, reader function, and contactless card function integrated into a chip, while RFID has two parts: reader and tag.
NFC technology can both read and write, while RFID can only achieve the reading of information and determination.
Second, the transmission distance is different. NFC transmission distance is much smaller than RFID, NFC transmission distance is only 10 cm, the RFID transmission distance can reach several meters or even tens of meters.
NFC is a close-distance private communication method, compared to RFID NFC has the characteristics of close distance, high bandwidth, low energy consumption, and high security.
Third, the application areas are different. NFC is more used in the field of consumer electronics, playing a huge role in access control, public transportation, cell phone payment, etc.; RFID is better at long-distance identification, more often used in production, logistics, tracking, and asset management.
Comparison of NFC and Bluetooth
NFC and Bluetooth are both short-range communication technologies. Compared to Bluetooth, which was integrated into cell phones early and has been popularized, NFC has only been integrated into cell phones in recent years, and so far only in a few cell phones.
First, the establishment time is different, the NFC communication setting procedure is simple, and communication establishment time is very short, only about 0.1s; while the Bluetooth communication setting procedure is relatively complex, the communication establishment time is longer, about 6s.
Second, the transmission distance is different, NFC transmission distance is only 10cm, while the Bluetooth transmission distance can reach 10m. but NFC is slightly better than Bluetooth in terms of transmission power consumption and security.
Third, the transmission speed and working frequency are different, the NFC working frequency is 13.56MHz, and the maximum transmission speed is 424 Kbit/s, while the Bluetooth working frequency is 2.4GHz, and the transmission speed can reach 2.1 Mbit/s.
Comparison of NFC and IR
NFC and infrared transmission are comparable in distance, but faster than infrared transmission, NFC transmission speed is up to 424 Kbit/s, while infrared transmission speed is about 100 Kbit/s.
The set-up time is slightly faster for NFC than IR, with an NFC set-up time of 0.1s and an IR transmission set-up time of 0.5s.
Infrared transmission must be strictly aligned in order to transmit data, and there can be no obstacles in between, while NFC does not have such restrictions; in addition, NFC is more secure and reliable than infrared.
What are the applications of NFC?
NFC is near-field communication technology, its application is very wide. NFC applications can be divided into four basic types, the following for the four basic application types to introduce and analyze.
Payment applications
NFC payment mainly refers to the application of NFC-enabled cell phones virtualized as a bank card, a card, etc. The application of NFC virtualization into a bank card is called an open-loop application.
Ideally, NFC-enabled cell phones can be used as bank cards for swiping at POS machines in supermarkets and shopping malls, but it is not yet fully realized in China.
The main reason is that NFC payment as an open-loop application has a lengthy industry chain, behind the interests of card vendors, and solution providers, and the industry pattern game is very complex.
In terms of the current domestic NFC open-loop application environment, due to the game of interests, NFC open-loop payment application has missed the best time before the popularity of mobile payments such as Alipay and WeChat Pay, NFC open-loop payment is no longer possible to develop alone.
NFC open-loop payment can only seek to connect and bundle with Alipay and WeChat Pay, and as a means of authentication for Alipay and WeChat Pay, it is possible to take a place in the future of mobile payment.
The application of NFC virtualized into a card is called a closed-loop application.
At present, the development of NFC closed-loop applications in the country is not very satisfactory, although in some cities the public transport system has opened the NFC function of cell phones, but not popular.
The fundamental reason is that the card-based card system has a profitable card issuance, and system integrators and operators (bus groups and schools, etc.) can make a good profit on card issuance.
So at present Xiaomi and Huawei are in some cities to pilot the opening of cell phones’ NFC bus card function, but at present are still required to open the service fee.
But with the popularity of NFC cell phone technology continuing to mature, a card system will gradually support the application of NFC cell phones, the prospect is optimistic, but the process is destined to be torturous.
Security applications
NFC security applications are mainly virtual cell phones into access cards, and electronic tickets.
NFC virtual access card is the existing access card data written into the phone’s NFC so that there is no need to use smart cards, using cell phones can achieve access control functions, so that not only is the configuration, monitoring, and modification of access control is very convenient and can achieve remote modification and configuration, such as temporary distribution of credentials card when needed.
NFC virtual electronic tickets are the application of the ticketing system after the user purchases a ticket to send the ticket information to the cell phone, NFC-enabled cell phones can virtualize the ticket information into an electronic ticket, in the ticket is directly brushed the phone can.
NFC in the security system is an important area of future NFC applications, the prospects are very broad. Because this area can directly bring economic benefits for the technology users, they have more incentive to upgrade existing equipment and technology.
Because of the use of cell phone virtual cards, you can reduce the use of access cards or magnetic card-type tickets, directly reduce the cost of use, in addition to the appropriate degree of automation, reduce personnel costs and improve efficiency.
Tag application
The application of NFC tags is to write some information into an NFC tag, the user only needs to use the NFC cell phone on the NFC tag to immediately obtain the relevant information with a wave.
For example, merchants can put NFC tags containing posters, promotions, and advertisements at the front of the store, and users can use their NFC phones to get the relevant information according to their needs and can log in to social networks and share details or goodies with friends.
Although NFC tags are very convenient and low-cost in application, with the current popularity of mobile networks and the gradual popularity of QR codes, the future of NFC tags application is not optimistic.
Because compared with NFC tags, QR codes only need to be generated and printed as a small image, which can be said to be almost zero cost and provide as much information as NFC is rich, and will easily replace the application of NFC tags.
What are the business features of NFC?
In recent years, NFC technology has received more and more attention, and the services developed based on NFC technology have gradually penetrated into all aspects of people’s lives.
NFC technology-based services have a short transmission distance because the data transmission is mainly based on the 13.56MHz frequency.
The information transmission based on NFC technology is triggered information transmission, and the information interaction time is very short, and much of the time during the operation is in milliseconds.
Therefore, according to the characteristics and advantages of NFC technology itself, the basic form of NFC-oriented services mainly has the following characteristics.
(1) Short: The communication distance is short, and the communication distance based on NFC is generally within 10 cm, which is generally within the reach of human hands.
(2) Frequency: as a short-range wireless communication technology, although not a new technology, but the past two years at home and abroad has been rapid development, and mobile payment as the representative of the NFC application is gradually deepened into people’s daily life, so the use of NFC-oriented business will become more and more frequent.
(3) Fast: the information transmission based on NFC technology is triggered information transmission, although the transmission rate is not high, often requires a very short time to complete the information interaction, so unlike other communication services, NFC-oriented business needs to be processed quickly.
Just because the business based on NFC technology has the characteristics of short operation distance, more frequent operation, and fast operation process, thus the limitations brought about in carrying out NFC-oriented business are as follows.
(1) Geographical limitations.
NFC technology operates at a short distance, mainly to establish a point-to-point data transmission between devices, unlike ordinary wireless transmission that requires the establishment of a wide range of transmission networks, so each region is able to establish a relatively independent business system and transmission system.
The existing NFC business status quo also proves this point, for example, the existing model of the public transportation system is a relatively independent business system in each city, and the city can not form interoperability between cities.
(2) Industry limitations.
NFC business entry threshold is low, each industry according to its own needs is easy to set up a specific business-oriented NFC system, and its own business operations.
(3) Business diversity.
For users themselves, NFC services are good for establishing a bridge between users’ real life and virtual life, which is often not limited by geography and industry.
What is NFC charging technology?
Based on the overall situation of patent applications for NFC technology in wireless charging currently available, its technical development trend is basically consistent with NFC technology.
Since NFC wireless communication technology has the disadvantage of very small transmission power and disadvantage in charging applications, NFC wireless charging technology even slightly lags behind the development of NFC technology.
NFC technology generally through the terminal to achieve its application, wireless terminal power endurance characteristics also belong to a major focus of research, and on this basis, wireless charging technology came into being.
For NFC wireless charging technology, on the one hand, there are improvements related to signature, authentication, and power efficiency derived from the characteristics of NFC technology itself.
On the other hand, since other wireless charging technologies, such as those based on electromagnetic induction and magnetic resonance, are relatively mature and complete, improvements in other wireless charging research areas are also applied to NFC charging technology, such as the adjustment of antenna forms and the study of electromagnetic shielding issues.
The development direction of the NFC charging antenna is roughly towards reducing interference, increasing communication distance, and miniaturization.
For miniaturization, terminal device shape, and other factors, the ring NFC antenna is used in a large number in the long term, and after 2010 with the further development of antenna technology, some three-dimensional structures, special geometry of the antenna also gradually applied to NFC charging.
For the demand of multi-band of terminal equipment, an antenna in the shape of the improvement of the dual structure of the ring NFC antenna appeared.
In this problem, more matching circuits are used to adjust, matching circuits are more diversified in the direction of adjustment, and at the same time can play a role in reducing the size of the antenna, enhancing the signal, and reducing interference.
Early management strategies were basically designed to reduce power consumption, but with the emergence of NFC charging technology, the strategies for power monitoring were transferred to the NFC charging strategy.
Among the technologies for monitoring the electrical characteristics of the terminal devices to rationalize charging, the one for monitoring the residual power was quickly proposed, and the one for initiating charging based on the distance of the terminal device from the charger appeared a little later, and both were extended to the multi-terminal domain in 2011.
This is relatively consistent with the pace of other wireless charging technologies when compared side-by-side. And for other technical parameters such as current and temperature that can be monitored, technical solutions for certain protection of the terminal were proposed.
C&T RF Antennas Inc manufactures 5G NR antennas, 4G LTE antennas, 3G UMTS GSM antennas, 2G GPRS NB-IoT antennas, LoRa/LoRaWan antennas (includes 169MHz antennas, 230MHz antennas, 315MHz antennas, 433MHz antennas, 868MHz antennas, 915MHz antennas), 2.4GHz 5GHz Wi-Fi antennas, GNSS antennas, GPS antennas, Cellular antennas, UHF VHF antennas, UWB antennas, etc.
And C&T RF Antennas Inc supplies the antenna accessories such as RF power amplifiers and repeaters, RF connectors and adapters, cable assemblies.
To help you select the best NFC antennas for your application, please contact us for more details such as the NFC antenna datasheet, NFC antenna pricing, NFC antenna inventory, or the NFC antenna styles.
Showing 1–16 of 28 results
-
13.56 MHz Flexible PCB NFC Antenna
Read more -
13.56 MHz Long Range Antenna Ipex Antenna
Read more -
13.56 MHz NFC Antenna Design
Read more -
13.56 MHz NFC Antenna PCB trace Antenna
Read more -
13.56 MHz NFC Antenna Tuning Flexible Antenna
Read more -
13.56 MHz NFC Chip Antenna Flexible Antenna
Read more -
13.56 MHz RFID Antenna Ipex Antenna
Read more -
13.56 MHz RFID Chip Antenna Ipex Antenna
Read more -
13.56 MHz RFID PCB Antenna NFC Antenna
Read more -
13.56MHz Antenna NFC PCB Antenna
Read more -
Flexible Antenna NFC 13.56 MHz Antenna
Read more -
Flexible NFC Antenna 13.56 MHz RFID Antenna
Read more -
High gain RFID Antenna 13.56 MHz Antenna
Read more -
High Gain RFID Antenna 13.56 MHz Flexible Antenna
Read more -
High-performance RFID 13.56 MHz NFC PCB Antenna
Read more -
Long Range NFC Antenna Flex PCB Antenna
Read more