
Recently, the R16 standard further supported the introduction of 5G LAN features, opening the pathway for integrating industrial IT and OT, making 5G+industrial Internet move toward low-cost and easy deployment, and accelerating the popularization of 5G on a large scale.
On July 3, 2020, the international standards organization 3GPP officially announced the freeze of the 5G R16 standard, which supports the unified global standard for ultra-reliable low latency communication (URLLC), compressing the end-to-end latency to less than 5 milliseconds and defining 5G LAN as an important accelerator to promote the expansion of 5G to vertical industries, kicking off the industrial 5G era in one fell swoop. 5G era in one fell swoop.
5G’s easy deployment, low latency, high reliability, large bandwidth, and wide connectivity characteristics can break the pain points encountered by traditional manufacturing transformation, such as cumbersome wiring, complex communication environment prone to interference, and more sensitivity to time delay and stability. On the contrary, the massive amount of data generated by the intelligent upgrade of production lines, equipment, and machines all over the factory also provides a favorable growth environment for 5G industry applications.
However, at the beginning of 5G’s bold reform in industrial manufacturing, it also faced the challenges of high cost and difficulty in quantity until the R16 standard further supported the introduction of 5G LAN functions, which opened up the pathway for the integration of industrial IT and OT, making 5G+industrial Internet move toward low cost and easy deployment, and accelerating the popularization of 5G on a large scale.
What is wireless 5G LAN?
5G LAN is a LAN built in a 5G network, through which a LAN with mobility can be assembled to meet production and office needs. 5G LAN has the benefit of cross-territory mobility, so even if two people are thousands of miles apart, they can still set up a LAN to achieve Layer 2 and 3 interoperability.
Simply put, 5G LAN uses 5G technology to group and build groups of terminals to form a LAN network. When using 5G cell phones, have you ever noticed that even if you and your friends are close together (even face to face), your phone cannot search each other? You can communicate with each other because the data flow to the carrier or Internet service provider’s server around the circle.
For the base station, all cell phone terminals are isolated. This is based on security considerations. Cell phones each use their channel without interference with each other.
LAN, on the other hand, connects terminals (cell phones, computers, etc.) in the area together into groups. This facilitates data transmission between each other and also saves external network outlets.
In LAN, terminals find each other by MAC addresses that can be addressed to each other (Layer 2 communication). A router can be routed in and out to access the external network through IP addressing (Layer 3 communication).
We all know that 4G changes life and 5G changes society. As the most mainstream mobile communication technology, 5G is tasked with interconnecting everything and helping the digital transformation of hundreds of industries and needs to help users in vertical industries open up connections.
Then, 5G can open the connection from each terminal to the cloud and realize the connection between terminals and terminals nearby.
Therefore, in the 3GPP R16 standard, a new feature function, 5G LAN, was introduced.
How does 5G LAN work?
Principles and features of 5G LAN
In a 5G network, the administrator can modify the data in the user database (UDM network element) to contract services to specified terminal (UE) numbers, thus grouping them into the same or different VN Groups (Virtual Network Groups).
The user database provides the VN Group information on terminal numbers and access policies to the management network elements (SMF, AMF, PCF, etc.) of the 5G core network (5GC). Based on this information and policy rules, the management network element forms them into different LANs. This is the 5G LAN.
Diagram of 5G LAN network architecture
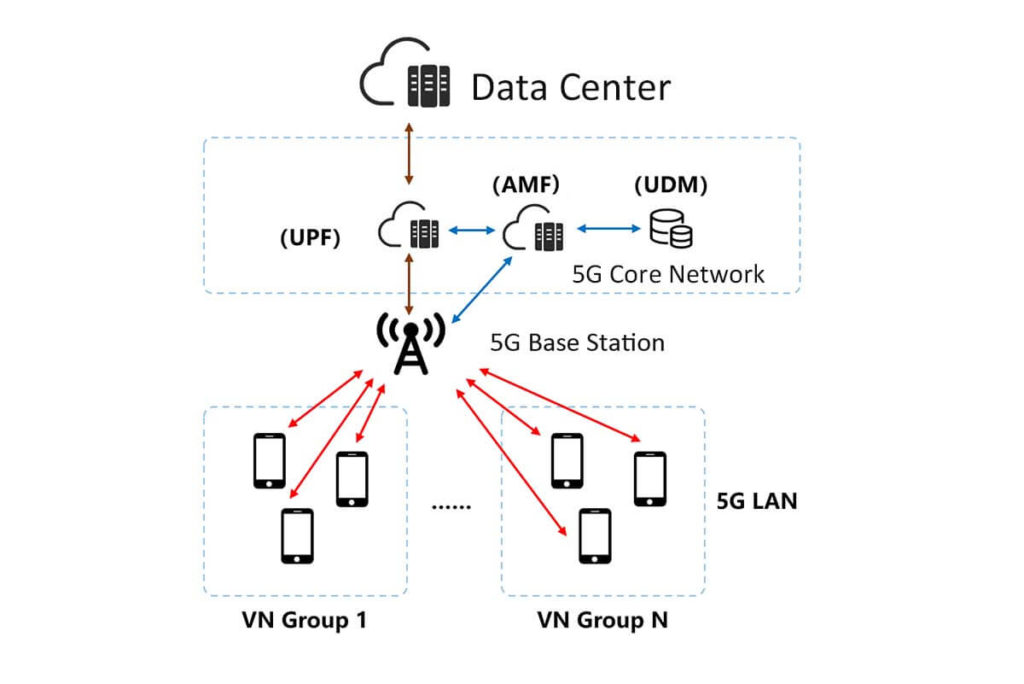
5G LAN supports Layer 2 communication (same network segment, direct access to each other) and Layer 3 communication (cross-segment, with the help of routing). 5G LAN supports unicast, as well as multicast and broadcast. In short, it is very flexible in how they access each other and simple to organize the network.
Regarding scope, 5G LAN supports mutual communication under the same UPF (media-plane network element of 5G core network) and different UPFs. This is equivalent to breaking the physical distance limitation between terminals.
The particularly important point is that the network established by 5G LAN can be connected to the user’s existing data network, thus enabling plug-and-play and mutual access.
What are the applications of 5G LAN?
5G LAN enables grouping and connectivity between designated 5G terminals, greatly facilitating enterprises to build a more mobile LAN network. Isn’t mobility already possible with the existing Wi-Fi technology? Why do we still need a 5G LAN?
The local networking enabled by 5G LAN can help enterprises, schools, government, homes, and other users to better interconnect terminals on a regional scale.
5G LAN can be used for office networks. However, its greater value lies in the transformation of the production environment of the campus and the transformation of the grassroots network of production-oriented enterprises such as industrial manufacturing, port terminals, and energy mines.
We are now all promoting the industrial Internet and believe that 5G can empower the digitization of industry scenarios because 5G has characteristics such as large bandwidth and low latency and is a superior wireless communication technology that enables wireless connectivity of various production elements in industrial scenarios.
Take industrial manufacturing as an example. Previously, industrial bus technology was used for better automation and equipment control. There are many types of this technology.
Later, with the emergence of Ethernet and IP technologies, the industrial community formed a consensus to evolve to Ethernet, and there was Industrial Ethernet. Now, no matter who has an industrial interconnection protocol, it is based on Ethernet.
Then later, industrial companies found that wired connections had too many restrictions on mobility – there was always an outgoing line behind the equipment, which prevented free movement.
Moreover, the wired connection was cumbersome to deploy, with long lead times and high costs. It’s also delayed to replace equipment or cables once they become faulty. Therefore, the industry began to consider the introduction of wireless communication technology.
Thus, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and other technologies entered the industrial field. If there is Wi-Fi, why do we need a 5G LAN?
The reasons are as follows.
What are the advantages of 5G LAN?
Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and other technologies entered the industrial field. If there is Wi-Fi, why do we need a 5G LAN?
The reasons are as follows.
First, the performance of Wi-Fi networks (especially Wi-Fi 4 and Wi-Fi 5) is not as good as 5G.
In terms of transmission rate and time delay, 5G can better meet the needs of industrial robots (robotic arm control), intelligent quality inspection (high-speed image recognition), AGV (unmanned logistics cart) and other scenarios.
Regarding coverage, 5G has a larger coverage area than Wi-Fi and can better cover the park. 5G’s intercellular switching capability, which is also stronger than Wi-Fi, can bring users a better network experience.
Second, Wi-Fi network maintenance costs are high.
Enterprises building campus Wi-Fi networks need to wire themselves and buy their equipment. The equipment has depreciation, damage, renewal, and dedicated maintenance. A huge amount of Wi-Fi equipment configuration is also very troublesome.
5G is different. It is built and maintained by the operator, and enterprises belong to rent (Wi-Fi compared to 5G, a bit like building your server room compared to cloud computing).
All things considered, 5G will be more cost-effective.
Third, the 5G LAN is more powerful.
5G LAN’s VN grouping, in addition to isolated communication, has a more important role is to achieve the quality of service differentiation of different networks.
For example, office networks, IT system networks, OT networks, etc., within the enterprise.
OT is Operational Technology operation technology (operational technology). It is a network that connects industrial environments and devices, such as lathes, robotic arms, sensors, instruments, AGVs, monitoring systems, MES, PLCs, etc.
Different networks have different performance requirements. Some need low latency, some need high bandwidth, and some are not as demanding.
Based on packetization, 5G LAN can define different network performances for different VN packets. Some enterprises call it “micro-slicing”.
Fourth, 5G LAN is easy to manage and more secure.
The operator’s 5G network can open the modification authority to the enterprise network manager by developing an interface to perform the self-service modification.
Of course, enterprises can also set their private network policies according to their needs.
When establishing data connections, enterprises can also establish authorization and authentication mechanisms for strictly managing VN groupings. This security is much more powerful and convenient than Wi-Fi.
Case Study of 5G LAN
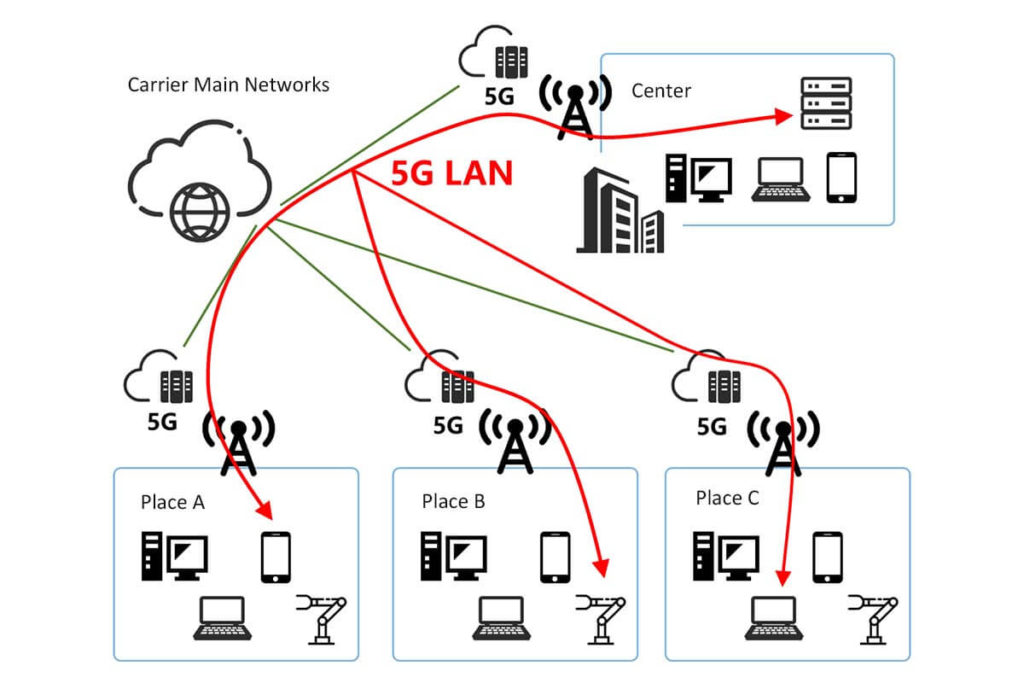
The plug-and-play capability of 5G LAN can perfectly integrate itself with the customer’s existing network, reducing the impact on the customer’s existing network and eliminating the need for laborious renovation and upgrade, which can save a lot of costs.
From a macro perspective, 5G LAN collaborates with 5G and Ethernet technologies. In the future, TSN (Time Sensitive Network) technology, which is developed based on Ethernet technology, cannot be developed without the help of a 5G LAN.
It is worth mentioning that 5G LAN can be used as a supplement to the traditional private line network of enterprises to connect off-site branch offices and facilitate the construction of internal campus networks.
Modules for 5G LAN
5G LAN is an important innovative technology for implementing 5G in vertical industries. It can build a more robust 5G private network communication and help customers accelerate digital transformation and upgrade.
To better deploy 5G LAN, in addition to network-side upgrades, 5G modules are also needed to support it.
Industrial Internet is the cornerstone of the fourth industrial revolution, and 5G private network technology innovation like 5G LAN is significant for the industrial sector to go digital, networked and intelligent across the board.
With the freezing of the 5G R17 version, we are gradually ushering in the 5G-Advanced era. New excitement continues, and new technological innovations, too, are emerging.
5G LAN commercialization triggers 5G industrial Internet boom
In the network deployment stage, on the one hand, 5G LAN realizes the decoupling of the carrier network and factory intranet, which significantly saves the cost of 5G industrial Internet network construction.
On the other hand, 5G LAN supports 5G native layer 2 networking, which can keep the enterprise’s original networking unchanged and significantly reduce the difficulty of 5G transformation of industrial production lines.
In the application scenario, 5G LAN can keep the enterprise IP autonomous allocation, reduce the tunnel equipment configuration, and realize the device plug-and-play.
Regarding communication capability, 5G LAN can achieve optimal local communication, optimal local switching delay, and optimal network load, further reducing the end-to-end delay of the industrial Internet.
As one of the key features defined by the R16 standard, 5G LAN is also gradually quantifying its disruptive significance for the 5G industrial era, becoming an important thrust for cost reduction and efficiency improvement in factories.
More importantly, outside the industrial field, 5G LAN is also exploring more application scenarios with its advantages of low cost, easy deployment, and low latency.
Besides this What is 5G LAN How Does It Work article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
How To Make a 433 MHz Yagi Antenna Design For A Long-range
55 Different Types of Antennas With Examples Used in Wireless Communication
4G vs. 5G: What is the difference between 4G and 5G?
How to Choose the Best Antenna for Lora?
