Description
What is a High-gain LTE 4G Antenna Internal Flexible PCB Antenna?
The High-gain LTE 4G Antenna CTRF-ANTENNA-FPC-7027-15227-IPEX is a flex PCB antenna, a 12/15dBi high-gain antenna, flexible Printed Circuit Board embedded FPC antenna designed by C&T RF Antennas Inc. for 4G LTE WiFi, GSM, CDMA, UMTS, ISM, SCADA, Utilities, IoT, NB-IoT, LoRa, LTE-IoT applications.
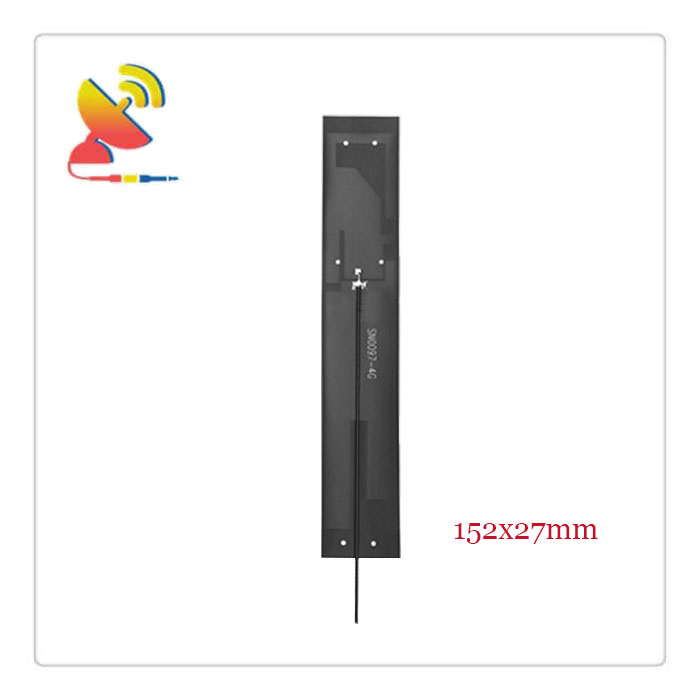
High-gain LTE 4G Antenna Internal Flexible PCB Antenna Item Model: CTRF-ANTENNA-FPC-7027-15227-IPEX
GSM 3G LTE 4G Built-in Antenna FPC Aerial with IPEX Connector High Gains 12/15dbi 700- 2700MHz Frequency GPRS 2G 3G 4G Antenna
C&T RF Antennas Inc. also provides High-gain LTE 4G Antennas with other antenna types.
C&T RF Antennas Inc provides internal & external antennas with antenna radio frequencies such as NFC, 169MHz, 230MHz, 315MHz, 433MHz, 868MHz, 915MHz, VHF&UHF, Lora, NB-IoT, ADS-B, GSM, GNSS, GPRS, 1.2 GHz, 1.4 GHz, 1.8 GHz, Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz, 5.8 GHz, Cellular 2G, 3G, 3.5 GHz, 4G LTE, GPS, 5G NR, 6G, etc.
C&T RF Antennas Inc. provides RF antennae with Omni & Directional antenna types such as Dipole Antennas, Whip Antennas, Marine Antennas, Router Antennas, MIMO Antennas, Combo Antennas, PCB Antennas, FPC Antennas, Spring Antennas, Magnetic Antennas, Sector Antennas, Yagi Antennas, and Accessories, etc, for IoT & M2M industries.
The High-gain LTE 4G Antenna Internal Flexible PCB Antenna is available at C&T RF Antennas Inc. Contact us for more details on the High-gain LTE 4G Antenna, such as High-gain LTE 4G Antenna datasheet, High-gain LTE 4G Antenna pricing, High-gain LTE 4G Antenna inventory, or other High-gain LTE 4G Antenna types.
High-gain LTE 4G Antenna Internal Flexible PCB Antenna Specifications:
High-gain LTE 4G Antenna Electrical Specifications |
|
| RF Antenna Type | Embedded FPC Antenna |
| Model | CTRF-ANTENNA-FPC-7027-15227-IPEX |
| Frequency | 700-960MHz, 1710-2700MHz |
| Gain | 12/15dBi |
| VSWR | ≤2.0 |
| Impedance | 50 Ω |
| Polarization | Vertical |
| Cable Type | RG1.13 |
| Connector | U.FL/IPEX |
| Cable Length | 100mm |
| Lightning Protection | DC-Ground |
High-gain LTE 4G Antenna Mechanical Specifications |
|
| FPC Board Dimension | 152x27mm |
| Weight | Approx. 10g |
| Material | Flexible PCB/FPC |
| Operation Temperature | -40˚C~+85˚C |
| Storage Temperature | -40˚C~+85˚C |
| Color | Black |
| Antenna Design | Dipole Array |
| Mounting | Adhesive Sticker/Connector |
| Safety, Emission, and other | RoHS Compliant |
| Applications | ISM/SCADA/Utilities, IoT/M2M/NB-IoT/LoRa, 2G 3G 4G LTE/LTE-IoT, GSM GPRS UMTS, etc. |
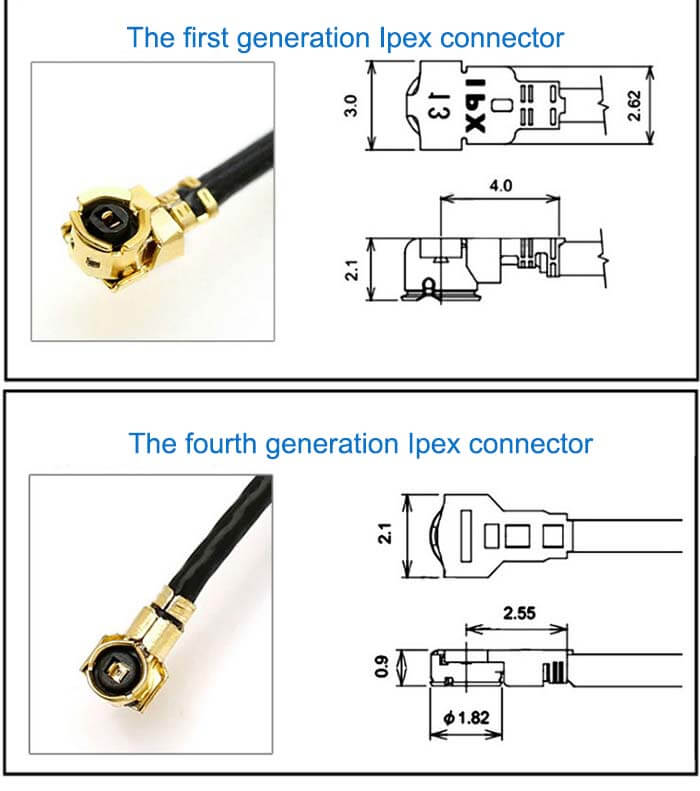
Flexible Antenna Features




High-gain LTE 4G Antenna Applications

What is 4G LTE technology?
LTE (Long Term Evolution) is the long-term evolution of the UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) technical standard formulated by the 3GPP (The 3rd Generation Partnership Project) organization. The project was formally established and launched at the 3GPP Toronto meeting in December 2004.
The LTE system introduces key technologies such as OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) and MIMO (Multi-Input & Multi-Output), which significantly increase the spectral efficiency and data transmission rate (20M bandwidth 2X2MIMO in the case of 64QAM.
The theoretical maximum downlink transmission rate is 201Mbps, after removing the signaling overhead, it is about 150Mbps, but according to the actual networking and terminal capacity limitations.
It is generally considered that the downlink peak rate is 100Mbps, and the uplink behavior is 50Mbps), and supports multiple bandwidth allocations: 1.4MHz, 3MHz, 5MHz, 10MHz, 15MHz and 20MHz, etc.,
And supports the global mainstream 2G/3G frequency bands and some new frequency bands, so the spectrum allocation is more flexible, and the system capacity and coverage are also significantly improved.
The LTE system network architecture is flatter and simpler, reducing network nodes and system complexity, thereby reducing system delays, and reducing network deployment and maintenance costs.
The LTE system supports interoperability with other 3GPP systems. According to different duplex modes, LTE systems are divided into FDD-LTE (Frequency Division Duplexing) and TDD-LTE (Time Division Duplexing).
The main difference between the two technologies lies in the physical layer of the air interface (like frame structure, time division design, synchronization, etc.).






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.