After reading this NB-IoT VS GSM comparison article, you will learn about:
The NB-IoT defines, features, and applications
The GSM defines, features, and the relationship between GPRS and GSM
The 6 comparisons of NB-IoT VS GSM:
- Comparison of NB-IoT VS GSM 1. Wide coverage
- Comparison of NB-IoT VS GSM 2. Massive connection
- Comparison of NB-IoT VS GSM 3. Low power consumption
- Comparison of NB-IoT VS GSM 4. Mobility is simplified
- Comparison of NB-IoT VS GSM 5. Half-duplex mode
- Comparison of NB-IoT VS GSM 6. NB-IoT deficiency

Here we go!
NB-IoT technology in the NB-IoT VS GSM
Narrowband IoT - Wikipedia

NB-IoT refers to Narrow Band Internet of Things (NB-IoT) technology, a low power wide area (LPWAN) network technology standard based on cellular technology for connecting various smart sensors and devices using wireless cellular networks, focusing on the low power wide coverage (LPWAN) Internet of Things (IoT) market, which is an emerging technology that can be widely used in a global It is an emerging technology that can be widely used worldwide.
NB-IoT technology is a simplified version of LTE technology, and the NB-IoT network is based on the existing LTE network for transformation.
LTE network serves people, cell phones, and consumer Internet; while NB-IoT network serves things, IoT terminals, and industrial Internet (IoT).
NB-IoT uses a License band and can be directly deployed in the GSM network, UMTS network, or LTE network to coexist with existing networks to reduce deployment costs and achieve smooth upgrades.
What is a Narrowband?
The network access speed of 64Kbps (maximum download speed of 8KB/S) and below is called narrowband, and the disadvantage of narrowband compared to broadband is the slow access speed.
What are the NB-IoT frequency bands?
| Band Number | Uplink (UL) /MHz | Downlink (DL) /MHz |
| Band 1 | 1920-1980 | 2110-2170 |
| Band 2 | 1850-1910 | 1930-1990 |
| Band 3 | 1710-1785 | 1805-1880 |
| Band 5 | 824-849 | 869-894 |
| Band 8 | 880-915 | 925-960 |
| Band 12 | 699-716 | 729-746 |
| Band 13 | 777-787 | 746-756 |
| Band 17 | 704-716 | 734-746 |
| Band 18 | 815-830 | 860-875 |
| Band 19 | 830-845 | 875-890 |
| Band 20 | 832-862 | 791-821 |
| Band 26 | 814-849 | 859-894 |
| Band 28 | 703-748 | 758-803 |
| Band 66 | 1710-1780 | 2110-2200 |
Note: Bank 3 in the table overlaps with the GSM DCS 1800 band, and Band 8 overlaps with the GSM 900 band, making it easy for GSM operators to upgrade to NB-IoT.
What are the characteristics of NB-IoT?
Low power consumption
NB-IoT focuses on small data volume and small rate applications, so the power consumption of NB-IoT devices can be very small, and the endurance of devices can be significantly increased from several months to several years.
Low Cost
NB-IoT is based on the technology of the LTE network, so it can be transformed on the basis of the existing LTE network so that the network can be set up quickly and the coverage can be expanded quickly. Major operators are still pushing hard to build LTE networks, which also facilitates the coverage improvement of NB-IoT.
Strong connection
With the same base station, NB-IoT can provide 50-100 times with the number of accesses than existing wireless technologies.
A sector is capable of supporting 100,000 connections, supporting low latency sensitivity, ultra-low device cost, low device power consumption and optimized network architecture. By placing more devices in a less large space without interfering with each other, NB-IoT is sufficient to easily meet the networking needs of a large number of devices in the future smart home.
Wide Coverage
NB-IoT has strong indoor coverage capability, with a 20dB gain over LTE, which is equivalent to a 100 times increase in coverage area capability. It can not only meet the demand for wide coverage in rural areas, but also for applications such as factories, underground garages and manhole covers that require deep coverage.
What are the communication protocols of NB-IoT?
NB-IoT is a communication technology, and the devices that use NB-IoT networks and IoT platforms to communicate generally have to comply with some kind of communication protocol, which is equivalent to two people talking on the phone, and the sound spreads through the airwaves, but the language used by these two people must be a language call that the other party can understand in order to be established.
The current mainstream communication protocols for communication between NB-IoT devices and IoT platforms are CoAP and LWM2M protocols.
Since most IoT devices are resource-constrained devices, their physical and network resources are very limited, and directly using the existing TCP and HTTP protocols for communication is too demanding for them.
For this reason, CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol) was designed to run on top of the UDP protocol, and its biggest feature is its small size, with the smallest packet being only 4 bytes.
CoAP is a complete binary application layer protocol that borrows the design of the HTTP protocol and simplifies the protocol packet format to reduce the learning cost for developers.
The LWM2M (Lightweight Machine-To-Machine) protocol is a CoAP-based IoT communication protocol proposed and defined by the OMA (Open Mobile Alliance).
LWM2M protocol defines the interface, object, and other specifications based on the CoAP protocol, which makes communication between IoT devices and IoT platforms more concise and standardized.
What are the applications of NB-IoT?
1). Public utilities:
Smart water meter, smart water service, smart gas meter, smart heat meter.
2). Smart city:
Smart parking, smart street light, smart garbage can, smart cellar well cover.
3). Consumer electronics:
Independent wearable devices, smart bicycles, chronic disease management systems, elderly and children management.
4). Equipment management:
Equipment status monitoring, white goods management, large public infrastructure, pipeline corridor safety monitoring.
5). Intelligent building:
Environmental alarm system, central air conditioning supervision, elevator IOT, human defense space coverage.
6). Command logistics:
Cold chain logistics, container tracking, fixed asset tracking, and financial asset tracking.
7). Agriculture and environment:
An agricultural Internet of things, animal husbandry breeding, real-time air monitoring, and real-time water quality monitoring.
8). Other applications:
Mobile payment, smart community, smart home, heritage protection.
About GSM Technology in the NB-IoT VS GSM

GSM concept
Global System for Mobile Communications, abbreviated as GSM, is a digital mobile communications standard developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Organization ETSI. Its air interface uses time division multiple access technology.
Since its commercial introduction in the mid-1990s, it has been adopted by more than 100 countries worldwide, and GSM-compliant equipment accounts for more than 80% of the current global market for cellular mobile communications equipment.
Since GSM is the second generation of mobile communication technology relative to analogue mobile communication technology, it is referred to as 2G.
What are the GSM frequency bands?
GSM system includes GSM 900: 900MHz, GSM1800: 1800MHz, and GSM1900: 1900MHz and several frequency bands.
Initially, the country allocated to the analogue mobile communication network frequency band [885-905MHz, 930-950MHz], a total of 20MHz.
Mobile GSM900 band is [905-909, 950-954MHz], a total of 4MHz; Mobile GSM1800 band is [1710-1720MHz, 1805-1815MHz], a total of 10MHz.
Unicom GSM 900 band is [909-915MHz, 954-960MHz], total 6MHz; Unicom GSM 1800 band is [1745-1755MHz, 1840-1850MHz], total 10MHz.
Later, when the analogue network was withdrawn, Mobile transferred 20MHz frequency resources from the original analogue network to GSM900 frequency, so Mobile GSM used a total of 34MHz frequency resources and Unicom used 16MHz.
The frequency bands acquired by China Mobile are 1880-1900 MHz and 2010-2025 MHz.
The frequency bands acquired by China Telecom are 1920-1935 MHz and 2110-2125 MHz.
The frequency bands obtained by China Unicom are 1940-1955MHz and 2130-2145MHz.
What are the features of GSM?
Spectrum efficiency
Due to the use of efficient modulators, channel coding, interleaving, equalization and voice coding technology, the system has high spectral efficiency.
Capacity
The GSM system can be reduced to 4/12 or 3/9 or even smaller (7/21 for analogue systems) due to the increased transmission bandwidth of each channel, which reduces the co-frequency multiplexing plant ratio requirement to 9 dB.
This, together with the introduction of half-rate voice coding and automatic call distribution to reduce the number of cross-zone switching, makes the capacity efficiency (number of channels per MHz per cell) of the GSM system three to five times higher than that of the TACS system.
Voice quality
Given the characteristics of digital transmission technology and the definition of the air interface and voice coding in the GSM specification, the voice quality always reaches the same level above the threshold value independent of the radio transmission quality.
Open interfaces
The open interfaces provided by the GSM standard are not only limited to the air interface but also the newspaper network directly and between the various equipment entities in the network, such as the A interface and the Abis interface.
Security
Security is achieved through the use of authentication, encryption and TMSI numbers. Authentication is used to verify the user’s right to access the network. Encryption is used for the air interface and is determined by the key of the SIM card and the network AUC.
TMSI is a temporary identification number assigned to the subscriber by the service network to prevent someone from tracking and leaking his or her geographic location.
Interconnection with ISDN, PSTN, etc.
Interconnection with other networks usually utilizes existing interfaces, such as ISUP or TUP, etc.
Roaming on the basis of SIM card. Roaming is an important feature of mobile communications, which marks the automatic access of users from one network to another.
Global mobile communication systems can provide global roaming, but of course, it also requires certain agreements between network operators, such as billing.
The relationship between GPRS and GSM
GPRS is a packet-switched data carrier and transmission method developed on the basis of GSM
GPRS is a packet-switched data bearing and transmission method developed on the basis of GSM, compared with the original GSM, GPRS has very obvious advantages in the bearing and support of data services.
GPRS can make more effective use of wireless network channel resources and is particularly suitable for bursty and frequent small traffic data transmission.
higher rates of data transmission supported by GPRS, with theoretical peaks of 115kbps.
GPRS billing is more flexible and can support billing by data traffic.
GPRS can also support voice calls while data is being transmitted.
etc.
Comparison of NB-IoT VS GSM, what are the differences?
Comparison of NB-IoT VS GSM 1. Wide coverage
Compared with traditional GSM, one NB-IoT base station can provide 10 times area coverage.
One NB-IoT base station can cover an area of 10km, and one base station in a small county can cover it.
Meanwhile, NB-IoT improves 20dB gain over LTE and GPRS base stations, and can cover places where signals are hard to reach, such as underground garages, basements, underground pipes, etc. It is impossible to have signals to make calls underground, but NB-IoT can still communicate!
Comparison of NB-IoT VS GSM 2. Massive connection
NB-IoT 200KHz frequency can provide 100,000 connections
The more connections provided, the fewer base stations are built, and the fewer base stations are built, the more money is saved! A base station can connect 200 devices at the same time, NB-IoT base station can connect 20 devices, so that under the same premise of connecting 1000 devices, the NB-IoT base station connecting 200 devices can employ only 5, while the GSM base station has to employ 50.
Comparison of NB-IoT VS GSM 3. Low power consumption
Use AA batteries (No. 5 battery) can work for ten years, no need to charge
NB-IoT introduced eDRX power-saving technology and PSM power-saving mode, further reducing power consumption and extending the battery life. In PSM mode, the terminal is still registered on the network, but the signalling is not reachable so the terminal stays in deep sleep for a longer time to achieve the purpose of power saving.
The eDRX power-saving technology further extends the sleep cycle of the terminal in idle mode, reducing the unnecessary start-up of the receiving unit, which significantly improves the downlink reachability compared to PSM.
What is eDRX?
DRX (Discontinuous Reception), that is, discontinuous reception. eDRX is extended discontinuous reception.
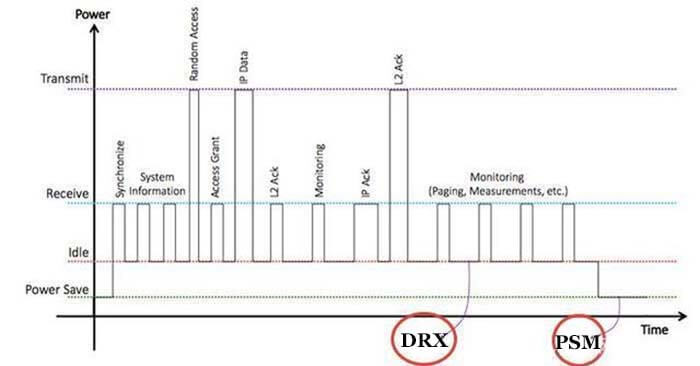
As shown in the figure, DRXs are discontinuous to receive signals, most of the time rest. For example, continuous reception is a security guard 24 hours a day can not leave the job, eyes to carefully stare at the door to see if there are no abnormalities occur. Discontinuous reception is a security guard who only spends ten minutes an hour watching the door, the rest of the time drinking tea and resting.
What is PSM?
PSM (Power Saving Mode), that is, power saving mode. Many IoT terminals have nothing to do most of the time, read the meter and send a meter word, and then they are done, and they can sleep after doing their work. The device enters the hibernation state.
The power saving of NB-IoT is like a security guard who has to rest and drink tea for 50 minutes within one hour of work, so that he only works for 3 hours a day and sleeps the rest of the time.
Comparison of NB-IoT VS GSM 4. Mobility is simplified
Unlike our cell phones, often in the car, on the high-speed railway, the high-speed railway call signal is not good, because the speed is too fast cell phone is constantly switching base stations, just like a relay race, the baton is well-connected call normal, the baton is lost, the call intermittent or even dropped.
For IoT terminals using NB-IoT, most scenarios are stationary, such as smart meter reading, which can reduce the complexity of the protocol and at the same time reduce the module cost.
Comparison of NB-IoT VS GSM 5. Half-duplex mode
Half Duplex data transmission means that data can be transmitted in both directions on one signal carrier, but not at the same time.
Comparison of NB-IoT VS GSM 6. NB-IoT deficiency
Deployment NB-IoT frequency is authorized and must be deployed by the operator! Want to build one yourself? At the moment it still seems not possible. It seems to want to make a one-time investment, and then no more money this road does not work.
The NB-IoT module is still high cost (compared to the mature GPRS/GSM module, and wifi module) this should be slowly reduced with the increase in use.
Besides this NB-IoT VS GSM, What is The Difference Between GSM and NB-IoT article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
4G vs. 5G: What is the difference between 4G and 5G?
How to Choose the Best Antenna for Lora?
