This article describes the 6 commonly used LPWAN technologies listed in the Internet of Things solutions.
Now the development of the Internet of Things is too fast, the landing application is also increasing, and the future direction of intellectual development is the Internet of Things. We need to understand some application technologies in the Internet of Things.
Definition of LPWA
LPWA – Low power wide area, short for low power wide area technology, using lower power consumption to achieve long-distance wireless signal transmission.
Compared with the familiar low-power Bluetooth (BLE), Zigbee, and Wifi technologies, LPWA has a much longer transmission distance, generally at the kilometer level, and its link budget (link budget) can reach 160dBm, while BLE and Zigbee are generally below 100dBm.
Compared with traditional cellular network technologies (2G, 3G), LPWA has lower power consumption, and battery-powered devices can last for several years. Based on these two distinctive features, LPWA can truly enable the Internet of Things (IoT) revolution.
LPWAN – Low power wide area network, i.e. a wireless connection network built with LPWA technology, LPWAN can be connected in various forms. A typical topology is shown in the below figure.
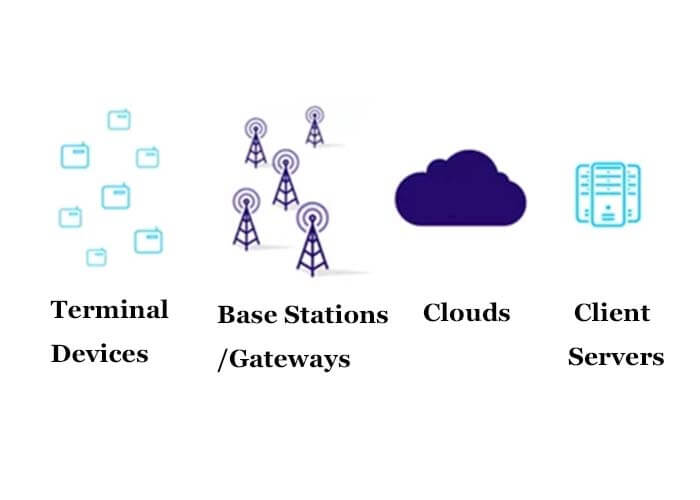
The base station or gateway receives and transmits the data to the cloud platform, which distributes the data to the corresponding client-server according to the device ID. For private LPWAN networks, the cloud and the client-server can be the same.
What are the features of LPWA technology?
LPWA technology has the following technical features for the needs of IoT applications.
Low power consumption
LPWA optimizes the technology to enable battery-powered devices to last for several years. For example, a terminal device using Sigfox technology can be powered by AA batteries for about 10 years.
Long distance
Wireless technologies such as low-power Bluetooth and Zigbee can be used for indoor or short-range IoT applications. LPWA targets outdoor or long-range wireless connectivity needs with lower transmission rate requirements, so the transmission distance is much longer, at least in the kilometre range.
Sigfox uses ultra-narrowband for data transmission and chooses a lower transmission rate, which allows the link budget (link budget) between the device and the base station to reach 160dBm, and the signal transmission distance in open areas can reach tens of kilometres.
Low cost
The popularity of new technologies cannot be separated from the continuous reduction of costs. Lower costs can make the technology used in more areas, especially for price-sensitive applications. RF modules for LPWA terminal devices are generally expected to be priced under $5 as technology maturity increases, applications become more popular, and device connections increase.
The Sigfox technology has reached commercial maturity very early, and its terminal module price can reach US$2, which plays an important role in popularising the technology.
o High capacity
The primary object of traditional wireless cellular networks is people. In contrast, the object of IoT is things, and the number of things will far exceed the number of people, which requires a larger capacity of LPWA networks to avoid network congestion and interference between devices.
A single base station of the Sigfox network can handle millions of device messages per day. It can receive and process close to 300 messages simultaneously with a packet loss rate of 0.5%, guaranteeing a high network quality of service (QoS).
In addition to the above significant technical features, LPWA is usually characterized by low rate and high latency.
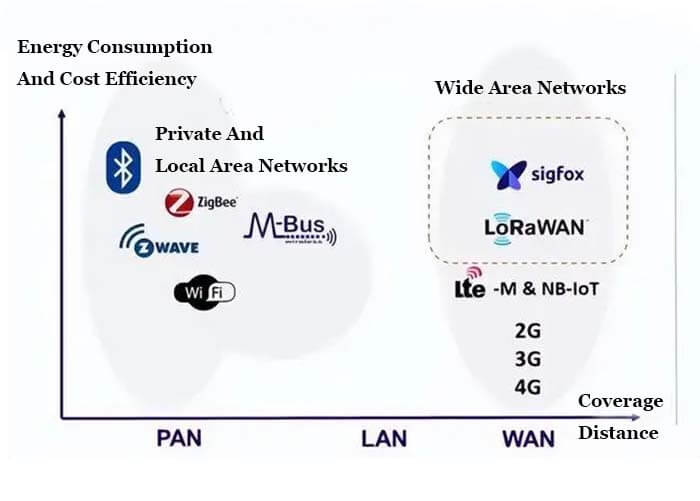
LPWAN can be used to build a private wireless sensor network. Still, it can also be a third-party-provided service or infrastructure, allowing the sensor owner to own the sensor without investing in the gate’s construction.
A wireless network refers to any radio computer network, commonly combined with telecommunications networks, which can be linked between nodes without needing cables. Wireless telecommunication networks are generally used in shaky information transmission systems that use electromagnetic waves, such as radio waves, as the carrier and physical layer of the network. For example:
– TD-LTE
– CDMA2000
– WCDMA
– TD-SCDMA
– CDMAOne
– GPRS
– EDGE
– GSM
– UMTS
– Wi-Fi
– WiMax
– ZigBee
One of the directions of wireless network development is “universal wireless network technology”, meaning that different wireless networks are unified under a single device. Wireless technologies.
What are the applications of LPWA technology?
LPWA technology can be used in many IoT application scenarios to achieve the digitization and intelligence of the industry, thus further improving efficiency and cost savings and promoting the improvement of labor productivity of the whole society.
Its typical applications are as the below showing.
◇Logistics positioning and tracking-real-time reporting of logistics location and status information
◇Asset management-asset positioning and inventory status reporting
◇Smart meter reading – reporting meter figures and status
◇Smart city-intelligent lighting, traffic, basic implementation testing, intelligent parking, etc.
◇Smart agriculture – livestock tracking and management, soil testing, intelligent irrigation, etc.
◇Environment/public utility-disaster detection, smoke detection, air pollution, equipment status, elderly care, etc.
◇Smart home – smart home appliances, home security system, status detection, reporting, etc.
IoT communication technology requires the ability to cover a wide range of networks with low power consumption, and LPWA is a wireless network technology suitable for the IoT era.
LPWAN Technologies List
What are the LPWAN Technologies Listed?
LPWAN Technologies Listed Light Modulation technology
Light Modulation — Let the light carry the sound and digital signals
Light Modulation technology is a Typical LPWA Technologies
LPWA can be classified into two types of technologies, licensed band and public band, according to the nature of the use of the wireless spectrum.
Typical public bands are Sigfox and LoRa, which use the public ISM band without paying for spectrum. However, there are still government regulations on the use of spectrum to ensure that different technologies are compatible, similar to BLE and Wifi.
Licensed bands are Cellular-IoT (C-IoT for short) technologies, which use specifically dedicated radio bands authorized by the government and require the payment of spectrum fees, with traditional telecom operators as the main deployment and operation of the network.
LPWAN Technologies Listed Sigfox technology
Sigfox technology is designed and developed by the eponymous French company Sigfox, founded in 2010. It is the earliest veteran LPWA player with the highest technical maturity and has been commercially operated in more than 60 countries worldwide as of 2019.
Sigfox uses a 100Hz ultra-narrowband spectrum in the public band to modulate and transmit data messages, so it has higher per unit band Sigfox uses 100Hz ultra-narrowband spectrum to modulate and transmit data messages in the common band, so it has a higher power density per unit band and is more resistant to interference and suitable for data transmission using the common band.
Sigfox provides complete network solutions, including base stations and cloud, seeking and relying on local partners for network deployment and operations worldwide.
Sigfox provides network equipment and technical support services. The terminal equipment is an open ecosystem, and any RF module or chip that supports the Sigfox protocol can connect to Sigfox’s network, allowing for greater choice and more favorable pricing options for terminal equipment manufacturers.
Relying on a strong global ecosystem, Sigfox users can get an end-to-end (end-to-cloud) total solution that enables their products to connect to the Sigfox network and be brought to market quickly.
Because the Sigfox network is deployed globally, led by Sigfox, this ensures maximum uniformity and stability of network quality of service, i.e., one global network, where user devices can enjoy the convenience of going across borders without roaming services and connect to the same quality network, which is particularly attractive for applications such as logistics or cross-border operations.
LPWAN Technologies Listed LoRa technology

LoRa is a proprietary technology of Semtech, a US-based company, and is a wireless modem technology using a spread spectrum solution; Semtech acquired the IP rights of LoRa in 2012 through the acquisition of Cycleo, a French company that designs and manufactures RF chips and markets them as a pure semiconductor company with a monopoly on the supply of LoRa chips.
Although Semtech also carries out a small amount of LoRa IP licensing, such as Ali in China, the IP is proprietary to Semtech, and no company can design and manufacture LoRa chips without authorization, so customers have very little choice.
LoRa also uses the public frequency band for RF signal transmission, and LoRaWan defines the upper layer protocols and specifications. The LoRa Alliance is responsible for publishing and maintaining them.
Anyone can buy LoRa chips or modules to design LoRa terminals and gateway devices and can also design or buy devices to build LoRa networks. Hence, most LoRa networks are currently small and private, and there are few national common IOT networks, and compatibility between devices and networks is also a big challenge.
LoRa achieves high sensitivity through spread spectrum technology, thus enabling long-distance transmission. Still, the limited network capacity prevents efficient parallel reception and processing of information from many devices, which is a great challenge for a large area or nationwide deployment.
LPWAN Technologies Listed LoRaWAN technology
The LPWAN Technologies Listed LoRa specifies only the physical layer, while LoRaWAN is a wireless communication network standard specified by the LoRa Alliance. Since it is specified as a wireless communication network, each company’s LoRaWAN base stations and LoRaWAN devices can communicate with each other.
In addition to installing and using self-owned base stations, it is possible to use LoRaWAN base stations installed by carriers. A usage contract with the operator is required to use the LoRaWAN base station installed by the operator.
LPWAN Technologies Listed Cellular-IoT technology
The current mainstream Cellular-IoT (C-IoT) technologies refer to NB-IoT and LTE-M, both based on traditional cellular network technologies, tailored and optimized for low-cost and low-power applications in IoT.
The technical specifications are defined and distributed by 3GPP, based on proprietary licensed spectrum and network deployment and operation by traditional telecom operators.
Since C-IoT is based on traditional cellular network technology, the technical complexity, cost, and power consumption will be higher than new LPWA customized technologies such as Sigfox, similar to 3G/4G, etc.
C-IoT terminal devices also need to connect and attach to the base station, protocol handshake, and network parameter configuration. In contrast, Sigfox terminal devices do not have any dependency on the base station, are more autonomous, and have controllable power consumption.
In addition, because of the attachment to the base station, NB-IoT only applies to the application scenario where the device location is fixed.
From a global perspective, C-IoT networks are decentralized, and each operator can only deploy and operate in its own country or region, with different network parameters and service quality.
The NB-IoT network, for example, supports more than ten bands in total, and networks in different countries or regions can use different bands, which is a higher cost and technical challenge for terminal devices.
The quality of service of different networks cannot be unified and guaranteed, and switching between networks also requires high roaming costs. NB-IoT networks do not even support roaming.
Besides this What are LPWAN Technologies Listed In IoT article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
4G vs 5G: What is the difference between 4G and 5G?
How to Choose the Best Antenna for Lora?
