Description
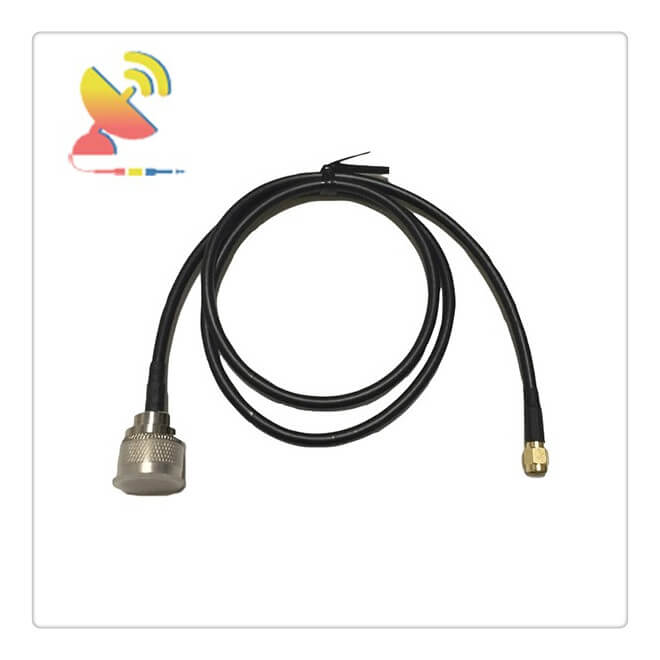
What is an SMA to N-Type Coaxial Cable Assembly RG58 Coax Cable Assembly?
The SMA to N-Type Coaxial Cable Assembly CTRF-CC-SMA-N-RG58-500 coaxial cable assembly comes with an SMA to N-Type male connector cable RG58 low loss coax cable antenna extender.
The low loss SMA to N-Type Male Cable, model CTRF-CC-SMA-N-RG58-500, extends your wireless antenna signal, to provide optimal placement.
The CTRF-CC-SMA-N-RG58-500 SMA to N-Type cable assembly can be used with wireless routers, access points, and adapters that feature a removable SMA antenna. Polyethylene jacketed cable designed for outdoor use.
C&T RF Antennas Inc provides internal & external antennas with antenna radio frequencies such as NFC, 169MHz, 230MHz, 315MHz, 433MHz, 868MHz, 915MHz, VHF&UHF, Lora, NB-IoT, ADS-B, GSM, GNSS, GPRS, 1.2 GHz, 1.4 GHz, 1.8 GHz, Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz, 5.8 GHz, Cellular 2G, 3G, 3.5 GHz, 4G LTE, GPS, 5G NR, 6G, etc.
C&T RF Antennas Inc. provides RF antennae with Omni & Directional antenna types such as Dipole Antennas, Whip Antennas, Marine Antennas, Router Antennas, MIMO Antennas, Combo Antennas, PCB Antennas, FPC Antennas, Spring Antennas, Magnetic Antennas, Sector Antennas, Yagi Antennas, and Accessories, etc, for IoT & M2M industries.
Contact C&T RF Antennas Inc. for more details on the SMA to N-Type cable assembly such as SMA to N-Type cable assembly pricing, SMA to N-Type cable assembly inventory, etc.
Key Specifications of the SMA to N-Type Coaxial Cable Assembly RG58 Coax Cable
| Item NO.: CTRF-CC-SMA-N-RG58-500 | |
| Connector Series 1 | SMA |
| Connector Gender 1 | Male |
| Connector Polarity 1 | Standard |
| Connector Angle 1 | Straight |
| Connector Mount Method 1 | None |
| Connector Impedance 1 | 50 |
| Connector Series 2 | N |
| Connector Gender 2 | Male |
| Connector Polarity 2 | Standard |
| Connector Angle 2 | Straight |
| Connector Mount Method 2 | None |
| Connector Impedance 2 | 50 |
| RF Cable Part Number | RG58 |
| RF Cable Type | RG58 |
| RG Cable Length | 200mm |
| Color | Black + Golden + Nickel |
| Frequency | DC 0-18Ghz |
| V.S.W.R | 1.5 |
| Voltage Breakdown | DC1000V/50Hz |
| Insertion Loss | ≤0.1dB/GHz |
| Insulation Resistance | ≥5000MΩ |
| Contact Resistance | Shell≤2.5mΩ; Center Pin≤3mΩ |
| Center Pin Retention | ≥50g |
| Mating Cycles | >500 |
| Operation Temperature | -40℃~+65℃ |
| Storage Temperature | -40℃~+80℃ |
| Junction Retention | ≥8KG |
Coaxial Cable
The coaxial cable is a guiding system composed of two coaxial cylindrical conductors, a broadband microwave transmission line filled with air, or a high-frequency medium between the inner and outer conductors.
Fundamental
The coaxial cable is a shielded and non-dispersive structure, and the main mode of the guided wave in the coaxial cable is TEM wave, but it can also transmit TE mode and TM mode at the same time, its cut-off frequency is zero, and the corresponding cut-off wavelength tends to infinity.
It is a two-conductor transmission cable composed of two coaxial inner and outer conductors and a dielectric in between.
Generally, the outer conductor of the coaxial line is grounded, and the electromagnetic field is confined between the inner and outer conductors, so the coaxial line has no radiation loss and is almost free from external signal interference.
Its working frequency band is wider than the two-wire transmission cable, and it can be used in a band larger than the centimeter wave.
Structural characteristics
The structure of the coaxial cable consists of four parts: jacket, outer conductor layer, insulating dielectric layer, and inner conductor from outside to inside.
The function of each part is introduced below.
The sheath, that is, the outermost layer is an insulating layer, which plays a protective role.
The outer conductor has a dual function as a shielding layer. It can conduct a low level through the transmission loop and has a shielding effect. The outer conductor usually has three structures.
1. Metal tube.
This structure is made of copper or aluminum strip longitudinal welding, or seamless copper pipe extrusion and drawing. This structure has the best shielding performance, but it has poor flexibility and is often used for trunk cables.
2. The aluminum-plastic composite tape is longitudinally wrapped.
This structure has a better shielding effect and low manufacturing cost, but because the outer conductor is a circular tube with longitudinal slits, electromagnetic waves will leak out through the slits.
3. Combination of woven mesh and aluminum-plastic composite belt longitudinal wrapping.
It is developed from a single woven mesh structure. It has the characteristics of good flexibility, lightweight and reliable joints. It adopts a reasonable composite structure and greatly improves the shielding performance. This structure is widely used.
The insulating medium, PE material, is mainly to improve anti-interference performance and prevent water and oxygen corrosion.
Inner conductor, copper is the main material of the inner conductor, which can be in the following forms: annealed copper wire, annealed copper tube, and copper-clad aluminum wire.
Usually, the inner conductor of the small cable is a copper wire or copper-clad aluminum wire, while the copper tube is used for the large cable to reduce the weight and cost of the cable. Tie the outer conductor of the large cable so that sufficient bending performance can be obtained.
The coaxial structure belongs to a two-conductor transmission line, which can establish an electromagnetic field distribution similar to a static field in its cross-section. One of the characteristics of a coaxial line is that it can be applied from the DC range to the millimeter-wave band.
The coaxial line is widely used in the design of broadband feeders and components mainly in TEM mode. When the wavelength of the transmission signal is much larger than the length of the transmission cable, the magnitude and phase of the current (or voltage) at each point on the transmission line can be approximately the same, and there is no need to consider the effect of distributed parameters.
But when the wavelength of the transmission signal is comparable to the length of the transmission cable, the magnitude and phase of the current (or voltage) at each point on the transmission line are different, showing a distributed parameter effect.
At this time, the transmission line must be treated as a distributed parameter circuit. It means that TE and TM modes will appear in the coaxial line, that is, the higher-order mode of the coaxial line.
Types of coaxial cable
According to the application position of coaxial cable, it can be roughly divided into 3 types.
1. Trunk cable
A thick cable whose insulation outer diameter is generally above 9mm, requires low loss and low flexibility.
2. Branch cables
Medium and thick cables whose insulation outer diameter is generally more than 7mm, require low loss and a certain degree of flexibility.
3. User distribution network cable
The insulation’s outer diameter is generally 5mm, and the loss requirement is not the main one, but it requires good flexibility indoor uniformity and coordination.
RF Cable Assembly Manufacturer Produced Similar Products










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.