Description
What is a High-gain Antenna Outdoor 4G Diversity LTE Antenna?
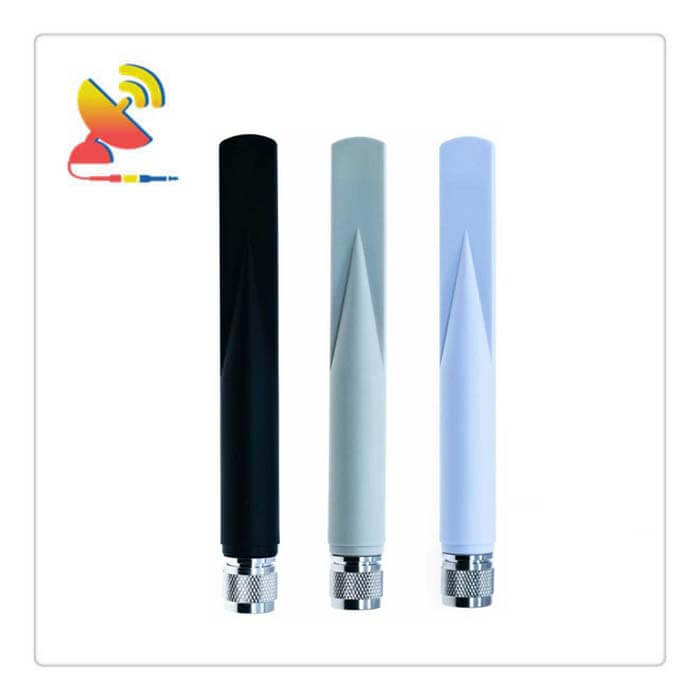
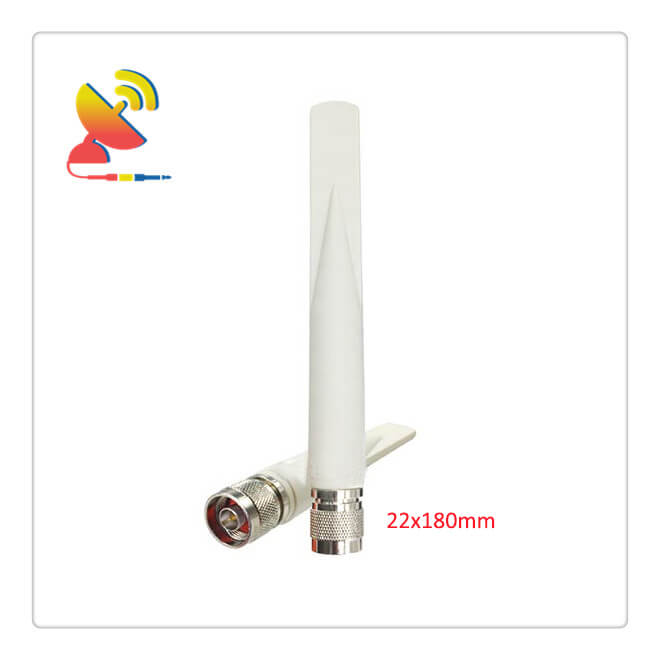
The High-gain Antenna Outdoor 4G Diversity LTE Antenna CTRF-ANTENNA-FRP-7027-22180-N model is a GFNR antenna 5dBi high gain antenna fiberglass antenna radome with an IP67 waterproof grade omnidirectional indoor-outdoor 4G LTE antenna manufactured by C&T RF Antennas Inc.
The High-gain Antenna Outdoor 4G Diversity LTE Antenna comes with an N-J standard N-male connector and a 22x180mm medium size for the wireless industry such as Lora, ISM, LTE, IoT, M2M, etc.
For this style, we also have the 433Mhz antenna frequency, Wi-Fi antenna frequency, GPS, GSM, etc.
We provide the IoT & M2M antennas with other radio frequencies such as 169MHz, 230MHz, 315MHz, 433MHz, 868MHz, 915MHz, Lora, NFC, VHF&UHF, NB-IoT, ADS-B, GSM, Wifi 2.4GHz, 5.8GHz, 2G 3G 4G LTE, GPS, GNSS, 5G NR, UWB, etc.
C&T RF Antennas Inc. also provides RF antennas with many antenna types, such as Dipole Antennas, Whip Antennas, Marine Antennas, Router Antennas, MIMO Antennas, Combo Antennas, PCB Antennas, FPC Antennas, Spring Antennas, Sector Antennas, Yagi Antennas, etc for IoT & M2M industries.
Contact us for more details on the High-gain Antenna Outdoor 4G Diversity LTE Antenna such as 4G Diversity LTE Antenna datasheet, 4G Diversity LTE Antenna pricing, 4G Diversity LTE Antenna inventory, or the other types of 4G Diversity LTE Antenna, thank you.
In this 4G Diversity LTE Antenna style, we have three colors Black/White/Grey for your choice.

High-gain Antenna Outdoor 4G Diversity LTE Antenna video
High-gain Antenna Outdoor 4G Diversity LTE Antenna Specifications
High-gain Antenna Outdoor 4G Diversity LTE Antenna Electrical Specifications |
|
| RF Antenna Type | Omnidirectional Antenna |
| Model | CTRF-ANTENNA-FRP-7027-22180-N |
| Frequency | 698-960MHz; 1710-2700MHz |
| Gain | 5dBi |
| VSWR | ≤2.0 |
| Impedance | 50 Ω |
| Polarization | Vertical |
| Horizontal Beam-width | 360 Degree |
| Connector | N-Male |
| Max Power | 50W |
| Radiation Pattern | Omnidirectional |
| Lightning Protection | DC Ground |
High-gain Antenna Outdoor 4G Diversity LTE Antenna Mechanical Specifications |
|
| Dimension | 22x180mm |
| Operational Humidity | <65% |
| Radome Material | Fiberglass |
| Storage Temperature Range | -40~+85°C |
| Working Temperature Range | -40~+80°C |
| Color | White/Gray |
| Antenna Form | Multi-Band |
| Mounting | Screw |
| RoHS | Compliant |
| Applications | ISM/SCADA/Utilities, IoT/NB-IoT/LoRa, 4G LTE/LTE-IoT, 2G/3G/GSM/GPRS/UNTS/DAS/PCS, etc. |
Diversity LTE Antenna technology
How to ensure the reliability of signal transmission links in mobile communication networks is an important indicator.
In order to achieve this goal, it can be achieved through a variety of technologies, from the analysis of three main factors affecting the signal power of the receiving end:
First, the propagation loss and dispersion in free space can be improved by increasing the transmitter power;
Second, the shadow fading caused by the undulation of terrain, and the occlusion of buildings and obstacles, which can be improved by the macro-diversity technology;
Third, the mutual influence of direct waves reflected waves, and scattered waves generated by various objects in the transmission path, that is, multipath fading and the loss caused by Doppler frequency shift can be improved by micro diversity technology.
It can be seen from the above analysis that diversity technology can play a great role in improving the performance of wireless transmission links.
Diversity technology is achieved by finding and using independent (at least highly uncorrelated) multipath signals in the natural wireless propagation environment.
If one wireless propagation path has experienced deep fading, and the other is relatively independent The path may still contain a strong signal, so two or more signals can be selected from multiple signals to be combined, which can improve the instantaneous signal-to-noise ratio and the average signal-to-noise ratio of the receiving end at the same time, generally by 20dB to 30dB.
Diversity technology is an anti-fading technology for mobile communication and a powerful receiving technology that can greatly improve the performance of wireless links with relatively low investment.
Diversity technology is to use two or more uncorrelated signals for processing. The collection of uncorrelated signals can be realized in three ways: space domain, time domain, and frequency domain. The specific implementation methods are as follows:
Firstly, space diversity.
Also called antenna diversity, it is a form of diversity that is used more in mobile communications. Simply put, it uses multiple receiving antennas to receive signals and then combine them.
In order to ensure the non-correlation of the received signal, this requires that the distance between the antennas is large enough. In an ideal situation, the distance between the receiving antennas is only half the wavelength λ.
Secondly, polarization diversity.
In a mobile environment, the horizontal and vertical paths in the air are uncorrelated, so the signal also exhibits uncorrelated fading characteristics.
This allows two antennas to be installed at the transmitting and receiving ends, one horizontally polarized antenna, and one vertically polarized antenna so that two unrelated signals can be obtained. This technology has obvious effects in improving the transmission efficiency of the link and increasing the capacity when the number of cellular mobile users increases sharply.
Third, angle diversity.
The signal is affected by the environment during the transmission process so that the received signal cannot be in the same direction. In this way, installing a directional antenna at the receiving end can get unrelated signals to be combined.
Fourth, frequency diversity.
In theory, the probability of uncorrelated channels producing the same fading is the product of their respective fading probabilities. Frequency diversity refers to the transmission of signals on more than one carrier frequency, and its principle is based on the fact that the same fading does not appear on frequencies outside the channel’s coherent bandwidth.
Compared with space diversity, this technology saves the number of antennas. The disadvantage is that it not only requires more spectrum resources but also requires several receivers equal to the number of channels used in frequency diversity.
However, for special services, this cost may be worthwhile. This technology is often used in line-of-sight microwave links in frequency division duplex (FDM) mode. In practical applications, there is a working model called 1:N protection switching mode.
Fifth, is time diversity.
For a randomly fading signal, if the amplitude is sampled sequentially, the two samples whose time interval is greater than the coherence time are not correlated with each other.
This technique refers to the repeated transmission of signals at time intervals exceeding the channel coherence time so that the signals received again have an independent fading environment, thereby producing a diversity effect.
The performance of time diversity is basically determined by the moving speed of the mobile station, that is to say, it is determined by the fading characteristics between repeated transmissions.
If the mobile station is stationary, the time diversity will be invalid, because the coherence time is the moving speed of the mobile station. Inversely proportional.
The practice has proved that when the moving speed of the mobile station is greater than 40 km/h, time diversity can achieve good results. This technology has been widely used in spread spectrum CDMA RAKE receivers to process multipath signals.
Outdoor Fiberglass Antenna Features




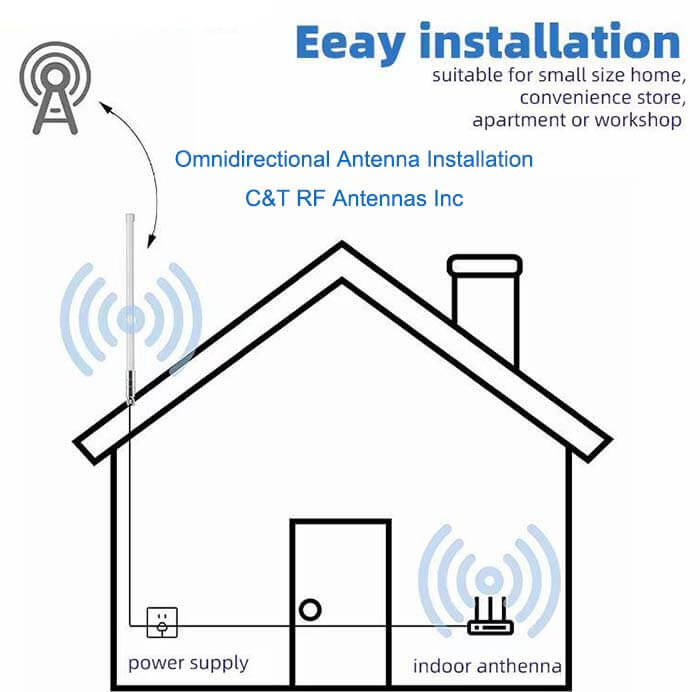
High-gain Antenna Outdoor 4G Diversity LTE Antenna Applications







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.