Description
What is External GPS Antenna GNSS Antenna Omni Rubber Antenna?
The GPS Antenna GNSS Antenna CTRF-ANTENNA-GPS-1575-13198-SMA is an External GPS Antenna GNSS Antenna Omni Rubber Antenna with a standard SMA male connector rubber antenna manufactured by C&T RF Antennas Inc.
The External GPS Antenna GNSS Antenna Omni Rubber Antenna comes with a hinge and bendable plastic rubber radome housing a 13x198mm size black color with an IP66 waterproof grade external antenna.
The External GPS Antenna GNSS Antenna Omni Rubber Antenna is available at C&T RF Antennas Inc.
C&T RF Antennas Inc provides internal & external antennas with the antenna radio frequencies such as NFC, 169MHz, 230MHz, 315MHz, 433MHz, 868MHz, 915MHz, VHF&UHF, Lora, NB-IoT, ADS-B, GSM, GNSS, Wifi 2.4GHz, 5.8GHz, Cellular 2G 3G 4G LTE, GPS, 5G NR, etc.
C&T RF Antennas Inc. provides RF antennae with Omni & Directional antenna types such as Dipole Antennas, Whip Antennas, Marine Antennas, Router Antennas, MIMO Antennas, Combo Antennas, PCB Antennas, FPC Antennas, Spring Antennas, Magnetic Antennas, Sector Antennas, Yagi Antennas, and Accessories, etc, for IoT & M2M industries.
Contact us for more details on the External GPS Antenna GNSS Antenna such as GPS Antenna GNSS Antenna datasheet, GPS Antenna GNSS Antenna pricing, GPS Antenna GNSS Antenna inventory, or other GPS Antenna GNSS Antenna styles.
External GPS Antenna GNSS Antenna Omni Rubber Antenna Specifications
External GPS Antenna GNSS Antenna Omni Rubber Antenna Electronical Specifications |
|
| RF Antenna Type | GPS Antenna |
| Model | CTRF-ANTENNA-GPS-1575-13198-SMA |
| Frequency | 1575.42 MHz |
| Gain | 3dBi |
| VSWR | ≤2.0 |
| Impedance | 50 Ω |
| Polarization | Right Hand Circular Polarization |
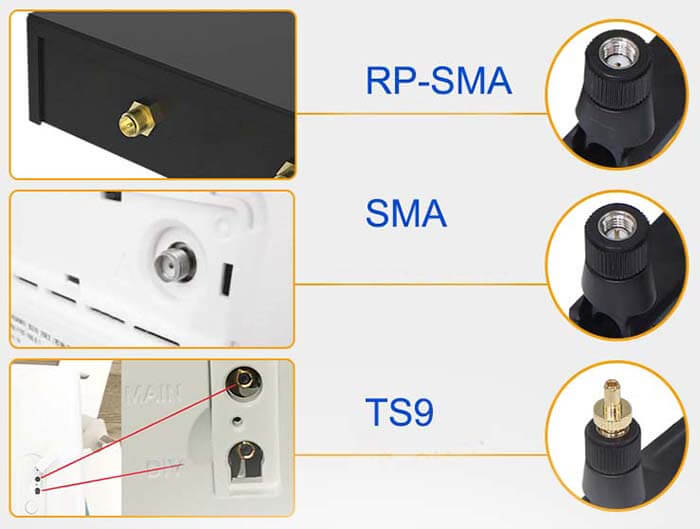
| Connector | SMA |
| Lightning Protection | DC Ground |
External GPS Antenna GNSS Antenna Omni Rubber Antenna Mechanical Specifications |
|
| Dimension | 13x198mm |
| Weight | Approx. 18g |
| Material | Plastic ABS |
| Operation Temperature | -40˚C ~ +85˚C |
| Storage Temperature | -40˚C ~ +80˚C |
| Color | Black |
| Antenna Form | Passive |
| Mounting | Screw/Connector |
| Safety Emission and other | RoHS Compliant |
| Applications | GPS/GNSS |
Omnidirectional Rubber Duck Antenna Features

GPS features
(1) Global all-weather positioning
The number of GPS satellites is large and evenly distributed, ensuring that at least 4 GPS satellites can be observed at any time anywhere on the earth, ensuring the realization of global all-weather continuous navigation and positioning services (except for the observation of thunder and lightning).
(2) High positioning accuracy
Application practice has proved that the relative positioning accuracy of GPS can reach 10-6m within 50km, 10-7m for 100-500km, and 10-9m for 1000km. In the 300-1500m engineering precision positioning, the plane position error is less than 1mm when observed for more than 1 hour.
Compared with the side length measured by the ME-5000 electromagnetic wave rangefinder, the side length difference is 0.5mm at most, and the error in the calibration is 0.3mm.
Real-time single-point positioning (for navigation): P-code 1~2m; C/A code 5~10m.
Static relative positioning: within 50km, the error is a few mm+(1~2ppm*D); above 50km, it can reach 0.1~0.01ppm.
Real-time pseudo-range difference (RTD): The accuracy reaches the decimeter level.
Real-time phase difference (RTK): accuracy of 1~2cm.
(3) Short observation time
With the continuous improvement of the GPS system and the continuous update of the software, the relative static positioning within 20km takes only 15-20 minutes; for fast static relative positioning measurement, when each rover is within 15 KM of the reference station, the rover observation time is only 1-2 minutes; when the real-time dynamic positioning mode is adopted, each station observation-only takes a few seconds.
Therefore, the use of GPS technology to establish a control network can greatly improve operating efficiency.
(4) There is no need to see between stations
GPS measurement only requires an open space over the stations and does not require mutual visibility between stations, so there is no need to build targets.
This advantage can greatly reduce the cost and time of measurement work (generally, the cost of standard construction accounts for about 30% to 50% of the total cost), and it also makes the selection of points very flexible, and it can also save the traditional measurement in the classic measurement. Counting points and measuring transition points.
(5) The instrument is easy to operate
With the continuous improvement of GPS receivers, the degree of automation of GPS measurement is getting higher and higher, and some have become “dumb”. During the observation, the surveyor only needs to install the instrument, connect the cable, measure the antenna height, and monitor the working status of the instrument.
Other observation tasks, such as satellite capture, tracking observation, and recording, are automatically completed by the instrument. When the measurement is finished, only need to turn off the power, put away the receiver, and complete the field data collection task.
If a long-term continuous observation is required on a measuring station, the collected data can also be transmitted to the data processing center through data communication to realize fully automated data collection and processing.
In addition, the volume of the receiver is getting smaller and smaller, and the corresponding weight is getting lighter and lighter, which greatly reduces the labor intensity of survey workers.
(6) Provide global uniform three-dimensional geocentric coordinates
GPS measurement can accurately determine the plane position of the station and the elevation of the earth at the same time. GPS leveling can meet the accuracy of fourth-level leveling.
In addition, GPS positioning is calculated in the global unified WGS-84 coordinate system, so the measurement results of different locations around the world are interrelated.
(7) Widely used






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.