What is 5G C band?
FCC voted to allocate a 3.7GHz-3.98GHz frequency C band for 5G services.
5G frequency spectrum

The frequency spectrum is the basic resource of wireless communication technology. In the future, the global 5G first frequency bands are C-band (spectrum range is 3.7GHz-4.2GHz, 4.4GHz-5.0GHz) and the millimeter-wave frequency band 26GHz/28GHz/39GHz. Accordingly, 3GPP has tailored n77, n78, n79, n257, n258, and n260.
5G uses a broadband method to define frequency bands, forming a few globally unified frequency bands, which greatly reduces the complexity of terminals (mobile phones) supporting global roaming. The maximum bandwidth of 5G has been increased from 20MHz to a maximum of 100MHz on the C-band and a maximum of 400MHz on the millimeter-wave.
It is equivalent to the width of the road, and the download or upload speed will be greatly improved. In addition, 5G uses more advanced symbol-shaping technology, such as Filter-OFDM, which reduces the overhead of the spectrum edge guard band. Compared with 4G, the transmission bandwidth has been significantly improved under the same nominal bandwidth.
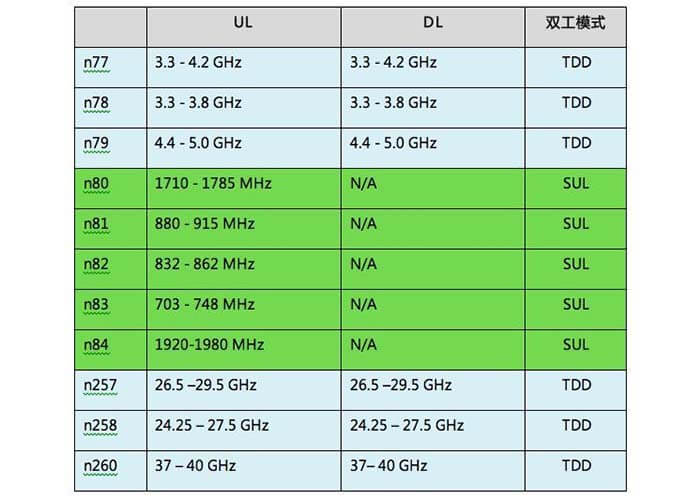
C band frequency spectrum in 5G
As expected, the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) passed a 3:2 vote to allocate the 280MHz spectrum in the C-band (3.7GHz-4.2GHz) for 5G services. At the same time, it will use existing satellites Services are reallocated to higher frequencies in this band.
The FCC chairman put a 3.7-4.2 GHz product on the agenda of the FCC public meeting in July to benefit many stakeholders in the terrestrial wireless industry.
The FCC voted to allocate the 3.7GHz-3.98GHz frequency band for 5G services. The frequency bands of the 5G network are divided into FR1 and FR2. Among them, the FR1 frequency band can be divided into Sub3GHz and C-band, and the C-band range is 3.7GHz- 4.2GHz.
According to the plan, the FCC will allocate the 3.7GHz-4.0GHz frequency band in the C-band for mobile services, of which 280MHz (3.7GHz-3.98GHz) will be auctioned by the FCC for US wireless services. In addition, 20MHz (3.98GHz-4.0GHz) will be used as a guide frequency band, and existing satellite service users will be packaged into the higher 200MHz frequency (4.0GHz-4.2GHz) of this frequency band.
The FCC has established a timetable and will convert the 280MHz spectrum on the C-band for flexible use no later than December 5, 2025.
According to FCC reports and orders, qualified satellite service operators will be able to receive $9.7 billion in accelerated spectrum clearance fees, provided they are willing to commit to doing so and successfully clear the spectrum as soon as possible.
To obtain the first phase of payment, satellite operators must clear the 120MHz spectrum of 46 partial economic areas (Partial Economic Areas) before December 5, 2021, and to obtain the second phase of payment, they must be in 2023. Clear the remaining 180MHz spectrum before December 5th.
However, in the C-Band Alliance, there are disputes over the allocation of these funds. Intelsat argued to the FCC that the company should receive 67% of the $9.7 billion, rather than the proposed 50%.
After the FCC voted on the C-band, it announced that making this critical frequency band available is another important step to eliminate the digital divide, especially in rural areas, and to ensure the United States’ leadership in the 5G field.
The Federal Communications Commission agreed to readjust more IF spectrum, including the 3.7-4.2 GHz band, which is commonly referred to as the C-band.
The C band of 3.7-4.2 GHz is regarded as a key link in the video distribution of cable TV program producers in countries and regions. It is used as a downlink for satellites, and the 6 GHz band is used for uplinks to satellites. C-band satellite transmission plays an important role in the video distribution ecosystem.
Besides the What is C Band In 5G article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
What is the difference between WIFI and WLAN?
Summary of 41 Basic Knowledge of LTE
What Is The 5G Network Slicing?
