Today, we talk about the Wi-Fi 5 Router VS Wi-Fi 6 Router.
With people’s dependence on the Internet, many families have paid attention to the construction of home networks, especially the popular Wi-Fi 6 technology in recent years, which has made many people wonder. Wi-Fi 6 is really so good?
Speaking of building a home wireless network environment, the current mainstream technologies are Wi-Fi 4, Wi-Fi 5, and Wi-Fi 6.
Should home users choose Wi-Fi 4 and Wi-Fi 5 when installing a new home network? Or choose Wi-Fi 6 technology? What is the difference between the three, and what changes in the wireless network experience can be brought to home users?
What is Wi-Fi 6?
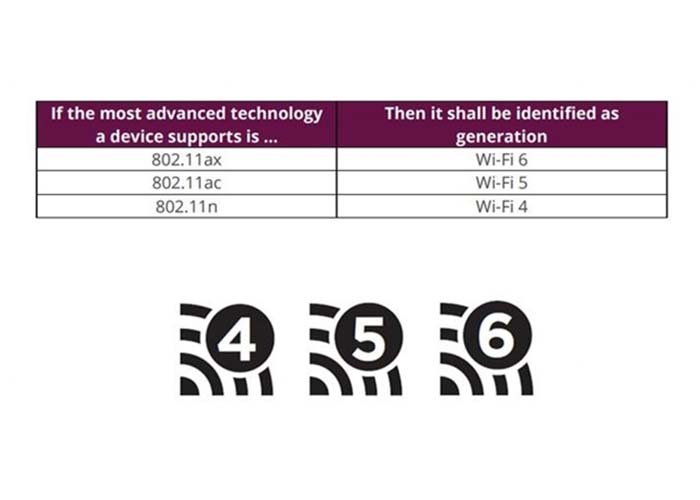
As the sixth-generation Wi-Fi technology, Wi-Fi 6 uses the 802.11ax standard.
In 2018, the Wi-Fi Alliance officially included Wi-Fi based on the 802.11ax standard in the regular army. Through the opportunity of promoting 802.11ax, the Wi-Fi specification was renamed, and the new standard 802.11ax was renamed Wi-Fi 6.
Not only has the naming convention changed, but also new icons have been adopted for Wi-Fi device network connections.
Technically, Wi-Fi 6 can support both 2.4G and 5G frequency bands, which is the true sixth-generation Wi-Fi iterative standard. Now it will also replace the 11n and 11ac products on the market.
In addition, Wi-Fi 6 also brings a full version of MU-MIMO (supports 8 terminal uplink/downlink), and at the same time introduces OFDMA technology to achieve another parallel transmission capability complementary to MU-MIMO. MU-MIMO is more flexible and practical.
Wi-Fi 5 router VS Wi-Fi 6 router, where are the advantages of Wi-Fi 6?
Compared to the previous generation Wi-Fi 5, the most prominent feature of Wi-Fi 6 is the substantial increase in speed.
The theoretical maximum speed of Wi-Fi 5 is 6.9Gbps, while that of Wi-Fi 6 is increased to 9.6Gbps, and the maximum speed is increased by nearly one-third.
This will greatly improve our daily internet speed. The higher the speed is most people’s first impression of Wi-Fi 6, but the advantages of Wi-Fi 6 do not stop there.
In addition to faster speed, better performance in crowded areas is another major advantage of Wi-Fi 6.
In layman’s terms, it is to solve the performance bottleneck when crowded, and you can get a smoother Internet experience when you have multiple devices. After all, multiple devices connected to Wi-Fi at the same time can easily cause network stalls.
And Wi-Fi 6 can solve this problem well. The reason is that Wi-Fi 6 uses OFDMA and MU-MIMO technologies.
Wi-Fi 5’s OFDM scheme is to dispatch vehicles on an order basis. Regardless of the size of the goods, one order is sent, and even a small piece of goods is sent to one car. This leads to low utilization of the carriages, low efficiency, and waste of resources.
Wi-Fi 6 using OFMDA technology can divide the wireless channel into multiple sub-channels to form a frequency resource block. User data is carried on each resource block instead of occupying the entire channel, achieving multiple sub-channels in each time period. Users transmit in parallel at the same time.
Compared with the previous generation technology, OFMDA technology orders are aggregated, and the trucks are loaded on the road as much as possible, which greatly improves transportation efficiency.
If OFMDA technology effectively improves the transmission speed, MU-MIMO technology realizes the parallel use of multiple users. Although Wi-Fi 5 also supports MU-MIMO, the router only allows communication with 4 devices at a time and only supports it. Downlink MU-MIMO.
The MU-MIMO technology carried by Wi-Fi 6 allows the router to communicate with up to 8 devices at the same time, and supports both uplink and downlink MU-MIMO, without sequential communication;
In contrast, the improvement from Wi-Fi 5 to Wi-Fi 6 is more like the expansion of one-way 4-lane to two-way 8-lane, and multiple devices are no longer like many vehicles waiting in line to exit from an exit, improved communication efficiency.
Wi-Fi 6, which supports TWT (Target Wakeup Time) technology, is more power-efficient, allowing APs to plan communication with devices and negotiate when and how often they will wake up to send/receive data.
Terminals can be grouped into different TWT periods, reducing the time required to keep the antenna powered on to transmit and search for signals, which means reducing power usage and also reducing the number of devices competing for wireless resources after waking up.
Wi-Fi 5 Router VS Wi-Fi 6 Router, Which one to choose?
After popularizing Wi-Fi 6 technology and its advantages, I believe you have a deeper understanding of Wi-Fi 6. Then as 5G with the same height as Wi-Fi 6, who has the advantage of the two?
Wi-Fi 6 and 5G are not a simple matter of choice but are limited by considerations of multiple factors such as time, space, and benefits.
As a technical solution to solve the localization of short-distance wireless transmission, including Wi-Fi 6, all protocols starting with 802.11 (including 802.11ax, ac, b, g, n, etc.) do not involve any control Spectrum resources. The frequency band where 5G is located is a spectrum resource regulated by the government established by the 3GPP and the communication associations of various countries.
Where the two are the same, Wi-Fi 6 and 5G also use OFDMA and MU-MIMO technologies, which have increased bandwidth and access capacity by as much as 4 times compared to their previous generations.
There are many differences between the two in essence. Wi-Fi 6 is actually a wireless technology with a smaller coverage area. The transmission power and use environment of the router determine the coverage area of Wi-Fi 6. Due to power and spectrum resource limitations, most routers are more suitable for covering an indoor scene.
The 5G network is a communication technology planned and managed uniformly by the country. It is generally deployed outdoors. Compared with Wi-Fi 6, it has a wider range and is less susceptible to interference. Therefore, 5G is mainly used in public network access and Internet infrastructure access.
Is the Wi-Fi 6 router really good?
Do I need to update my home router now? Although Wi-Fi 6 is good, users should refer to their own use environment and need before purchasing.
The wireless standard supported by the router at home is out of date. If it supports Wi-Fi 4 or lower, we recommend that you directly upgrade the router at home to a new product that supports the Wi-Fi 6 standard in one step.
After all, nowadays, newly released mobile phones and laptops, and other devices Wi-Fi 6 have become standard.
On the whole, Wi-Fi 6 router products can provide users with a smoother Internet experience, and at the same time have a good geographical complementarity with 5G. If you change to a Wi-Fi 6 router, you will definitely get a different feeling.
Besides the Wi-Fi 5 Router VS Wi-Fi 6 Router article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
What is the difference between WIFI and WLAN?
Summary of 41 Basic Knowledge of LTE
What Is The 5G Network Slicing?
