After the read of The Difference Between LTE-FDD and LTE-TDD, you will learn about
What is 4G?
What is LTE-FDD?
What is LTE-TDD?
The difference between LTE-FDD and LTE-TDD
What is 4G?
4G is the fourth-generation mobile phone mobile communication standard, which refers to the fourth-generation mobile communication technology, including TD-LTE and FDD-LTE.
LTE stands for Long Term Evolution technology, which is the abbreviation of English Long Term Evolution. LTE is technically considered 3.9G.
But we usually call them 4G because they have a data download capability of 100Mbps (referring to cat3 downstream bandwidth), which is about 10 times the current 3G network speed. It is also a key process for the evolution from 3G to 4G.
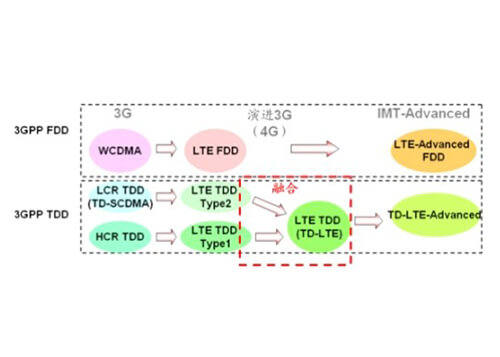
The LTE standard consists of two different duplex modes, TDD and FDD.
What is LTE-TDD and LTE-FDD?
TDD stands for Time Division Duplex, which means that uplink and downlink are interleaved on the same frequency band according to time allocation; while FDD is simultaneous on different frequency bands for uplink and downlink.
Although these two systems are nominally evolved from TD-SCDMA and WCDMA, in fact, LTE (including TDD and FDD) uses OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) to modulate the downlink, and SC-OFDM (single carrier) Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing).
This is a far cry from the standard of the 3G era. What it inherits, you can even think of it as two duplex modes: time division and frequency division.
At the same time, these two systems both use MIMO (Multiple Transmit and Multiple Receive) antenna technologies, and can also support 1.4, 3, 5, 10, 15, and 20 MHz signal bandwidths, and support the reuse of used frequency resources.
LTE has the advantages of high-speed uplink and downlink, efficient spectrum utilization, flexible system layout, and lower wireless access delay.
What is the difference between LTE-FDD and LTE-TDD?
The main difference between FDD and TDD lies in the use of different duplex modes. Frequency division duplex (FDD) and time division duplex (TDD) are two different duplex modes.
FDD is to receive and transmit on two separate symmetrical frequency channels and use guard bands to separate the receive and transmit channels. The disadvantage of FDD is that it must use paired frequencies, relying on frequency to distinguish between uplink and downlink, and its unidirectional resources are continuous in time. Although FDD can make full use of the uplink and downlink spectrum when supporting symmetric services, the spectrum utilization rate will be greatly reduced when supporting asymmetric services.
TDD uses the time to separate the receive and transmit channels. It is carried out in one channel. In a TDD mobile communication system, different time slots of the same frequency carrier are used for reception and transmission as the channel bearer, and time resources are allocated in two directions.
In a certain period of time, the base station sends a signal to the mobile station, and the mobile station sends a signal to the base station in the middle time interval. The base station and the mobile station must be coordinated to work smoothly.
In theory, the advantage of FDD is greater than that of TDD, which makes many potential 4G users excited and determined to use China Unicom’s LTE-FDD.
However, as far as the current form is concerned, the network using China Mobile or China Unicom Telecom is not too much. In terms of network coverage, the coverage of LTE-TDD is much greater than that of LTE-FDD.
Regarding the speed of 4G, whether it is LTE-TDD or LTE-FDD, it has a very good speed, enough for current users. And there is not much need for users to change operators in order to experience the difference between FDD and TDD.
Besides The Difference Between LTE-FDD and LTE-TDD article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
What is the difference between WIFI and WLAN?
Summary of 41 Basic Knowledge of LTE
What Is The 5G Network Slicing?
