Today, we talk about the LTE Cat 1 vs Cat 4. After the read, you will know about the difference between LTE Cat.1 and Cat.4.
To distinguish between LTE Cat.1 and Cat.4, we need to know what Cat is. Cat stands for Category, and the numbers after Cat represent the different categories, which 3GPP names in the Cat.
Cat. X is used to describe the capability level of user terminals according to the 3GPP Release definition, and Cat4 and Cat1 are both standards for user terminal categories in LTE networks for 4G communications.
What is Cat.1?
The full name of Cat.1 is LTE UE-Category 1, where UE refers to User Equipment, which is a classification of the wireless performance of user terminal equipment under the LTE network. According to the definition of 3GPP, the UE-Category is divided into 15 classes from 1 to 15.
Cat.1 in LTE Cat 1 vs Cat 4 is a 4G LTE network category, which can be called a low version of a 4G terminal with a 5Mbit/s uplink peak rate and 10Mbit/s downlink peak rate, and belongs to cellular IoT, a wide area network.
Cat1 in LTE Cat 1 vs Cat 4 supports the low and medium-rate IoT market together with NB-IoT with its advantages of low cost and low power consumption.
What is Cat.4?
Cat.4 in LTE Cat 1 vs Cat 4 is the full name of LTE UE-Category 4, which means the ue-Category of LTE is set to 4. The ue-Category refers to the level of UE’s access capability, the level of transmission rate that UE can support.
Cat4 in LTE Cat 1 vs Cat 4 can meet the communication needs of mobile broadband, but in some small size, battery-powered applications and application scenarios with poor network coverage, it cannot meet the communication needs of some IoT devices.
So 3GPP added several enhanced standards to LTE technology for connecting IoT devices, among which.
- LTE Cat.1 in LTE Cat 1 vs Cat 4 rate of 10Mbps, low power consumption compared to Cat4. Has the same millisecond transmission delay as LTE Cat.4, as well as support for mobile speeds of more than 100KM/H.
- LTE Cat.M2 (NB-IoT) rate is only a few hundred Kbps, power consumption has strong advantages, but cannot meet the voice and mobility needs.
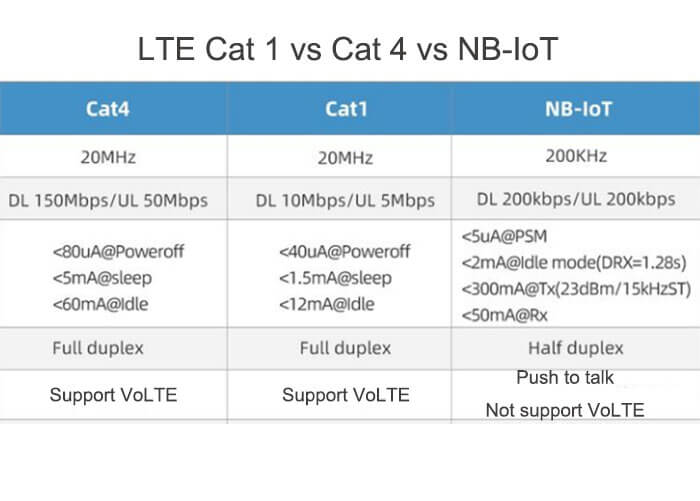
Parameters for LTE Cat 1 vs Cat 4
Comparison of Cat.1 and Cat.4
- Cat.1 has more cost advantages.
For example, in-network construction, LTE Cat.1 can now be seamlessly connected to existing LTE networks without hardware and software upgrades for base stations, resulting in low network coverage costs.
In terms of chip cost, after system optimization, the integration is higher, the hardware architecture of the module is simpler, and the peripheral hardware cost is lower.
Taking Cat1 and Cat4 modules with character networking as an example, the price of the Cat1 module is only about 1/3 of that of the Cat4 module.
- Cat.1 has the same advantages as Cat.4 in terms of speed, latency, and mobility.
It has the same millisecond transmission latency as LTE Cat.4 and supports mobile speeds of 100 km/H or more.
- Cat.1 has more application advantages.
Since Cat.1 is part of the 4G series, it can directly reuse existing 4G resources.
The migration from Cat.4 to Cat.1 has obvious benefits. For example, in scenarios where 4G is used for voice interaction, such as walkie-talkies and toy robots, the previous Cat.4 can be switched to Cat.1.
Many scenarios will have Cat.1 in play for voice functions as well as medium-rate connections. These scenarios include sharing, financial payment, industrial control, in-vehicle payment, public network intercom, POS, etc.
Application for Cat 1 in LTE Cat 1 vs Cat 4
Wearable devices, smart home appliances, industrial sensors, detection of hydrology and water resources, and port logistics tracking. They have a shared payment class. For broadband, rate requirements are not high, and at the same time, are battery-powered. Requirements for power consumption and data transmission stability are high.
Application for Cat 4 in LTE Cat 1 vs Cat 4
Vehicle networking, smart grid, 4G wireless routing, video security, commercial display equipment, 4G law enforcement instrument. Live video equipment. For broadband, rate requirements are very high at the same time, higher requirements for stability.
IoT application scenarios are wide, and the use of a complex environment, and users should choose the most suitable products according to their actual needs and site conditions.
Why is Cat.1 so popular?
- The inevitability of 2G/3G decommissioning: With the decommissioning of 2G and 3G becoming an inevitable choice, the IoT technology based on 4G/5G (NB-IoT+4G+5GNR) will take up the big task of opening up the Internet of everything.
- Construction of 5G and better utilization of frequency bands: cell phones and other mobile terminals will eventually migrate to 4G/5G and above networks, 2G/3G frequency bands are idle, 4G frequency bands are shared by 5G, and in order to better utilize spectrum resources, then network access capability needs to be developed for the many IoT devices with network demand.
- NB-IoT cannot meet the demand of medium-rate and mobile characteristics
- Cat. 4 is too small and costly
- Cat.1’s own advantages
- Common LTE Cat.4 cannot meet the communication needs of some IoT devices.
LTE was originally designed to address one overriding need; it had to be fast enough.
Although the technology can meet the needs of mobile broadband communication, it cannot be used well in some application products, such as wearable devices, industrial sensors, household appliances, etc.
Such devices are characterized by small size, and battery power and are often placed in places such as basements where network coverage is poor or even no signal.
Besides the LTE Cat 1 vs Cat 4 article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
What is the difference between WIFI and WLAN?
Summary of 41 Basic Knowledge of LTE
What Is The 5G Network Slicing?
