9 kinds of electromagnetic simulation software and methods, do you know what are they?
There are many different algorithms in computational electromagnetics, such as finite difference method in time-domain (FDTD), finite integral method in the time domain (FITD), finite element method (FE), moment method (MoM), boundary element method (BEM), spectral-domain method (SM), transmission line method (TLM), mode-matching method (MM), transverse resonance method (TRM), line method (ML) and analytical method, etc.
In the frequency domain, the numerical algorithms are Finite Element Method (FEM – Finite Element Method), Method of Moments (MoM – Method of Moments), Difference Method (FDM – Finite Difference Methods), Boundary Element Method (BEM – Boundary Element Method), and the Transmission-Line-matrix Method (TLM).
In the time domain, the numerical algorithms are Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD), and Finite Integration Technology (FIT).
These methods include analytical, semi-analytical, and numerical methods. The numerical methods are divided into zero-order, first-order, second-order, and high-order methods.
In descending order of resolution, they are finite difference methods in time-domain (FDTD), transmission line method (TLM), finite integration method in the time domain (FITD), finite element method (FEM), moment method (MoM), line method (ML), boundary element method (BEM), spectral-domain method (SM), mode-matching method (MM), transverse resonance method (TRM), and analytical method.
The analytical method, semi-analytical method, and numerical method were ranked according to the accuracy of the results from highest to lowest.
Among the numerical methods, the higher to lower accuracy of the results are higher-order, second-order, first-order, and zero-order.
Finite difference method in time-domain (FDTD), finite integration method in the time domain (FITD), finite element method (FEM), moment method (MoM), transmission line method (TLM), and line method (ML) are purely numerical methods; boundary element method (BEM), spectral-domain method (SM), mode-matching method (MM), and transverse resonance method (TRM) are all with high resolution.
The mode matching method (MM) is a semi-analytical method if the transverse mode of the transmission line is accurately available. Theoretically, the modes can be continuous spectra.
Due to the limitation of numerical solution accuracy, the transverse modes are usually required to be discrete spectra. This requires the transverse structure to be non-dissipative. In more general terms, this means a dissipation-free waveguide structure.
In other words, MM is most suitable for waveguide cavities, high Q, and a certain homogeneity of the structure in one dimension of energy transfer. For example, it is suitable for the analysis of the coupling of two cylindrical cavities in the height dimension, but not for the analysis of the coupling between two hoists, because the latter do not have very clear modes involved in energy exchange, and one can only consider a large number of modes together, which reduces the utility of MM.
The finite element method (FEM) is a first-order purely numerical method (if first-order elements are used). It is applicable to any shape of the structure and is a general method. But things are always divided into two.
In general, general-purpose methods will not be as efficient as special methods in special applications. For the high Q cavity filter design, MM is much better than FEM.
With the influence of computational electromagnetics in engineering applications, there is more and more commercial EM analysis software with intelligent operation interfaces, which makes it more convenient and intuitive for designers to design filters, antennas, and target EM characteristics.
Microwave software based on the finite element method, including ANSYS HFSS
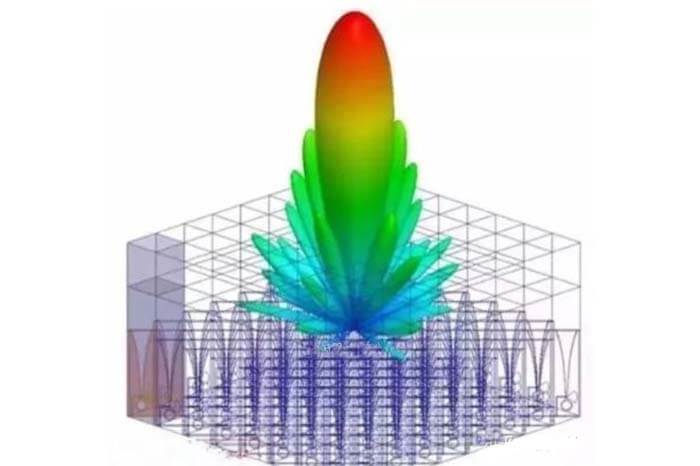
Electromagnetic Simulation Software 1, Ansys HFSS
ANSYS HFSS is the world’s first commercially available three-dimensional structural electromagnetic field simulation software, and is recognized as the industry standard for three-dimensional electromagnetic field design and analysis.
HFSS provides a simple and intuitive user design interface, a precise and adaptive field solver, and a powerful post-processor with unprecedented electrical performance analysis capabilities to calculate the S-parameters and full-wave EMF of any shaped 3D passive structure.
HFSS software has powerful antenna design functions, and the filter microcomputer thinks it can calculate antenna parameters, such as gain, directivity, far-field directional map profile, far-field 3D map, and 3dB bandwidth; plot polarization characteristics, including spherical field components, circularly polarized field components, Ludwig third defined field components and axis ratio. Using HFSS, it is possible to calculate.
① Numerical solutions and open boundary problems for basic electromagnetic fields, near and far-field radiation problems;
② Port characteristic impedance and transmission constants;
③ S-parameters and normalized S-parameters of the corresponding port impedances;
④ Eigenmode or resonance solution of the structure. Moreover, Ansys HFSS and Ansys Designer, the only physical prototype-based high-frequency design solution, provide fast and accurate design tools from system to circuit to component level, covering all aspects of high-frequency design.
Microwave software based on the finite integration method includes CST Microwave Studio
Electromagnetic Simulation Software 2, CST MICROWAVE STUDIO
CSY German Computer Simulation Technology launched a high-frequency three-dimensional electromagnetic field simulation software. Widely used in mobile communications, wireless communications (Bluetooth systems), signal integration and electromagnetic compatibility, and other fields.
CST simulation software contains the following main products: CST Microwave Studio, CST Design Studio, CST EM Studio, and MAFIA (MAFIA).
It is a simulation software for passive microwave devices and antennas, which can simulate couplers, filters, circulators, isolators, resonant cavities, planar structures, connectors, EMC, IC packages, all kinds of antennas and antenna arrays, and can give results such as S-parameters, antenna orientation diagrams, gain, etc.
MICROWAVE STUDIO is simple to use and provides users with intuitive electromagnetic characteristics for their high-frequency designs.
In addition to the main time-domain solver module, MICROWAVE STUDIO also provides eigenmode and frequency domain solver modules for some special applications.
The import of CAD files and the extraction of SPICE parameters enhance the design possibilities and shorten the design time. In addition, the open architecture of MICROWAVE STUDIO provides links to other simulation software, allowing MICROWAVE STUDIO to be integrated with other design environments.
Electromagnetic Simulation Software 3, Microwave Office
Microwave EDA software from AWR provides the most complete, fastest, and most accurate solution for microwave planar circuit design.
It is used to simulate and emulate microwave planar circuits through two simulators. For circuits consisting of aggregate components, the circuit approach is easier to handle;
The software has a “VoltaireXL” simulator to deal with microwave planar circuit problems consisting of aggregate components. For the specific microstrip geometry of the distributed parameter microwave planar circuit is composed of the field method is more effective;
The software uses the “EMSight” simulator to deal with any multilayer planar structure with three-dimensional electromagnetic fields. VoltaireXL” simulator has a library of components that can be used to model microwave circuits, including passive components such as inductors, resistors, capacitors, resonant circuits, microstrip lines, ribbon lines, coaxial lines, etc., and nonlinear components such as bipolar transistors, field-effect transistors, diodes, etc.
The “EMSight” simulator is a three-dimensional electromagnetic field simulation package for the analysis of planar high-frequency circuits and antenna structures. It features a combination of modified spectral-domain momenta and an intuitive windowed graphical user interface (GUI) technology, making calculations much faster.
MWO can analyze the electrical characteristics of circuits such as radio frequency integrated circuits (RFICs), microwave monolithic integrated circuits (MMICs), microstrip patch antennas, and high-speed printed circuits (PCBs).
Electromagnetic Simulation Software 4, ADS
Advanced Design System, a microwave circuit and communication system simulation software launched by Agilent, is one of the most used software in universities and research institutes in China.
Its functions are very powerful, simulation means are rich and diverse, can realize including time domain and frequency domain, digital and analog, linear and nonlinear, noise and other simulation analysis means, and the design results can be finished rate analysis and optimization, thus greatly improving the design efficiency of complex circuits, is a very excellent microwave circuit, system signal link design tools.
The main applications are RF and microwave circuit design, communication system design, DSP design, and vector simulation.
Electromagnetic Simulation Software 5, Ansys Designer
Ansys is a microwave circuit and communication system simulation software; it uses the latest windowing technology, is the first high-frequency circuit system, layout, and electromagnetic field simulation tools seamlessly integrated into the same environment of the design tool.
The key to this integration does not simply interface integration, but Ansys Designer’s unique on-demand solver technology, which allows you to select solvers as needed to achieve complete control over the design process.
Ansys Designer implements a WYSIWYG automated layout function, and the layout is automatically synchronized with the schematic, greatly improving the efficiency of layout design.
At the same time, the filter microcomputer that Ansys can also be easily integrated with other design software, and can be connected to test instruments to complete a variety of design tasks, such as frequency synthesizers, phase-locked loops, communication systems, radar systems, as well as amplifiers, mixers, filters, phase shifters, power dividers, synthesizers, and microstrip antennas.
The main applications are RF and microwave circuit design, communication system design, board and module design, and component design.
Electromagnetic Simulation Software 6, XFDTD
XFDTD is a 3D full-wave electromagnetic field simulation software based on the finite-difference time-domain method (FDTD) introduced by Remcom.
The software was first used to simulate cellular phones, long for cell phone antenna and SAR calculation. Now it is widely used in wireless, microwave circuits, radar scattering calculation, chemical, optical, land-based alert radars, and biological tissue simulation.
Electromagnetic Simulation Software 7, Zeland IE3D
IE3D is an EM field simulation tool based on the method of moments, which can solve the current distribution problem of 3D metal structures in the multi-layer media environment.
IE3D can be divided into three parts: MGRID, MOODUA, and PATTERNVIEW; MGRID is the pre-processing suite of IE3D, with the functions of establishing the circuit structure, setting the parameters of substrate and metal material, and setting the simulation parameters;
MOODUA is the core execution suite of IE3D, which can execute the simulation calculation of electromagnetic field, performance parameters (Smith diagram, S-parameters, etc.) calculation and execute parameter optimization calculation;
PATTERNVIEW is the post-processing suite of IE3D, which can display the simulation results, EM field distribution in the form of contour or vector field.
IE3D simulation results include S, Y, Z parameters, VWSR, RLC equivalent circuit, current distribution, near-field distribution and radiation direction map, directionality, efficiency and RCS, etc.;
The application scope is mainly in the analysis and design of microwave RF circuits, multilayer printed circuit boards, planar microstrip antenna design.
Electromagnetic Simulation Software 8, Sonnet
Sonnet is an EM simulation software based on the method of moments, providing EDA tools for 3D planar high-frequency circuit design systems as well as in the field of microwave, millimeter-wave, and EMC/EMI design.
SonnetTM is applied to planar high-frequency electromagnetic field analysis from 1MHz to several thousand GHz.
The main applications are microstrip matching networks, microstrip circuits, microstrip filters, ribbon line circuits, ribbon line filters, vias (connection or grounding of layers), coupled line analysis, PCB board circuit analysis, PCB board interference analysis, bridge screw inductors, planar high-temperature superconducting circuit analysis, millimeter-wave integrated circuit (MMIC) design and analysis, circuit analysis for mixed matching, HDI and LTCC conversion, accurate analysis of single or multi-layer transmission lines, circuit analysis of multi-layer planar, analysis of single or multi-layer planar antennas, analysis of planar antenna arrays, analysis of planar coupled holes, etc.
Electromagnetic Simulation Software 9, FEKO
FEKO is the abbreviation of German Feldberechnung bei Korpern mit beliebiger Oberflache.
FEKO is a powerful 3D full-wave EM simulation software from EMSS and is the first commercial software in the world to bring the method of moments to market. It is commonly used for electromagnetic field analysis of complex-shaped 3D objects.
FEKO is a professional EMF analysis software developed for antenna design, antenna layout, and EMC analysis, based on the classical Method Of Moment (MOM) from the strict EMF integral equation.
The MLFMM (Multi-Level Fast Multipole Method) algorithm is adopted to greatly improve the calculation efficiency while maintaining accuracy.
and seamlessly combines the momentum method with the classical high-frequency analysis methods (Physical Optics PO: Physical Optics, Uniform Theory of Diffraction UTD: Uniform Theory of Diffraction).
Thus, it is very suitable for analyzing various electromagnetic field analysis problems in antenna design, radar scattering cross-section (RCS), open domain radiation, and electromagnetic compatibility.
The Feko version after 5.0 is even mixed with the Finite Element Method (FEM: Finite Element Method), which can deal with multi-layer dielectric (such as multi-layer dielectric radome) and biological absorption rate problems more accurately.
Feko usually deals with the problem in the following way: for electromagnetic field problems such as antennas with electrically small structures, FEKO uses the full method of moments for the analysis, which ensures the high accuracy of the results.
For structures with a mixture of small and large electrical dimensions, FEKO can use both the highly efficient multi-layer fast multipole method based on the method of moments and the appropriate hybrid method after decomposing the problem (e.g., analyzing the small electrical structure partly by the method of moments and multi-layer fast multipole, and the large electrical structure part by the high-frequency method), thus ensuring a perfect combination of high accuracy and high efficiency, and unparalleled speed and accuracy in dealing with large electrical dimensions problems such as antenna design and RCS calculations.
Using the above technical route, Feko can choose different methods for different specific problems to carry out fast and accurate simulation analysis, which makes the application more flexible and applicable to a wider range, breaking through the limitation that a single numerical calculation method can only be limited to a certain type of electromagnetic problems.
What is free electromagnetic simulation software?
For these 9 kinds of electromagnetic simulation software, they will have the electromagnetic simulation software free version for the beginners, contact the electromagnetic simulation software supplier for more details.
Besides the 9 Kinds of Electromagnetic Simulation Software article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
What is the difference between WIFI and WLAN?
Summary of 41 Basic Knowledge of LTE
What Is The 5G Network Slicing?
