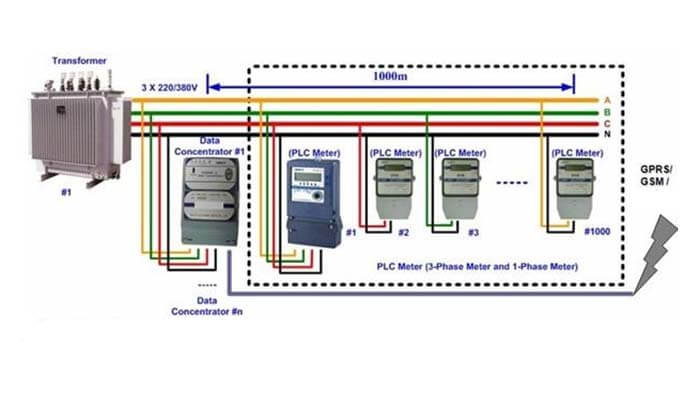
The PLC network is composed of several levels of subnets. The communication process of each level of the subnet is determined by the communication protocol, and the communication mode is the core content of the communication protocol. Communication methods include access control methods and data transfer methods.
The so-called access control (also called access control) method refers to the problem of how to obtain the right to use the shared communication medium, and the data transmission method refers to the problem of how to transmit data after a station obtains the right to use the communication medium.
Cycle I/O communication method
The periodic I/O communication method is often used in the remote I/O link of the PLC. The remote I/O link works in a master-slave mode, the PLC remote I/O master unit is the master station, and the other remote I/O units are all slave stations.
Set up a remote I/O buffer in the master station, adopt the mailbox structure, and divide it into several sub-boxes corresponding to each slave station. Each sub-box is divided into two compartments, one for sending and one for managing receiving.
The communication processor in the master station adopts a periodic scanning method, exchanges data with each slave station in sequence, sends the data sent in the corresponding sub-box to the slave station, and reads the data from the slave station, and puts it into the corresponding sub-station. In the receiving compartment of the box. This goes over and over again so that the remote I/O buffer in the master station is periodically refreshed.
The CPU unit of the PLC in the master station is responsible for the scanning of the user program. It is processed in a cyclic scanning mode. Each cycle has a period of time for centralized I/O processing. At this time, it performs the processing of the local I/O unit and the remote I/O. The buffer is read and written.
The periodic scanning of the user program by the CPU unit of the PLC and the periodic scanning of the remote I/O units with the PLC communication processor is carried out asynchronously.
Although the PLC’s CPU unit does not directly operate the remote I/O unit, because the remote I/O buffer is periodically refreshed, the PLC’s CPU unit reads and writes the remote I/O buffer, which is equivalent to direct access A remote I/O unit has been added. This communication method is simple and convenient, but it takes up the I/O area of the PLC, so it is only suitable for communication with a small amount of data.
The global I/O communication method
The global I/O communication method is a serial shared memory area communication method, which is mainly used for communication between PLCs with a link area.
The communication principle of the global I/O mode is shown in Figure 7-27. In the I/O area of each PLC in the PLC network, a block is drawn as the link area, and each link area adopts a mailbox structure.
The sending area with the same number is the same size as the receiving area, occupying the same address segment, one is the sending area, and the others are all receiving areas. Use broadcast communication.
PLC1 broadcasts the data in the 1# sending area on the PLC network, and PLC2 and PLC3 will receive it and store it in their 1# receiving area after listening.
PLC2 broadcasts the data in the 2# sending area on the PLC network, and PLC1 and PLC3 receive it and store it in their respective 2# receiving areas.
PLC3 broadcasts the data in the 3# sending area on the PLC network, and PLC1 and PLC2 receive it and store it in their 3# receiving area.
Through the above-mentioned broadcast communication process, the data in each link area of PLC1, PLC2, and PLC3 are the same, and this process is called the equivalence process. Through equivalence communication, the data in the link area of each PLC in the PLC network is kept consistent. It contains not only the data sent by itself but also the data sent by other PLCs.
Since the link area of each PLC is the same size and occupies the same address segment, as long as each PLC accesses its own link area, it is equivalent to accessing the link area of other PLCs, which is equivalent to exchanging data with other PLCs. In this way, the link area becomes a veritable shared storage area, and the shared area becomes an intermediary for each PLC to exchange data.
The link area can be refreshed asynchronously (equalization) or synchronously. The asynchronous mode refresh has nothing to do with the user program in the PLC. The communication processors of each PLC carry out the broadcast communication in order, repeating the cycle to keep all the link areas equal; the synchronous mode refresh is initiated by sending an instruction to the link area in the user program Refresh once. In this way, it is refreshed only when the data in the sending area of the link area changes.
In the global I/O communication mode, the PLC directly uses the read-and-write instructions to read and write the link area, which is simple, convenient, and fast. However, it should be noted that the write operation to a certain address in one PLC only applies to the same address in other PLCs. Can be read. Like the periodic I/O method, the global I/O method also occupies the I/O area of the PLC, so it is only suitable for communication with a small amount of data.
Master-slave bus communication mode
The master-slave bus communication method is also called the 1:N communication method, which means that there are N stations on the PLC subnet of the bus structure, of which there is only one master station, and the others are slave stations.
1:N communication mode adopts centralized access control technology to allocate bus usage rights, usually using the polling table method. The so-called polling table is a list of the order of the slave numbers. The table is configured in the master station. The master station inquires the slave stations according to the order of the polling table to see if it wants to use the bus, so as to allocate the right to use the bus. the goal of.
For stations with high real-time requirements, the slave number can appear several times in the round-robin table to give the station a higher communication priority. In some 1:N communication, the polling table method is combined with the interrupt method, and the emergency task can interrupt the normal periodic polling and obtain priority. To
In the 1:N communication mode, there are two data transmission modes when the slave station obtains the right to use the bus. One is to allow only master-slave communication, but not slave-slave communication. To exchange data between the slave station and the slave station, it must be transferred through the master station; the other is to allow both master-slave communication and slave-slave communication and the slave station obtains the use of the bus. After the right, arrange the master-slave communication first and then arrange the communication between itself and other slave stations.
The token bus communication method
The token bus communication method also called the N: N communication method means that there are N stations on the PLC subnet of the bus structure, and their status is equal, and there is no distinction between the master station and the slave station. It can also be said that N stations are all master stations.
N: N communication mode uses token bus access control technology. A logical ring is formed on the physical bus, and a token flows sequentially in a certain direction in the logical ring, and the station that obtains the token obtains the right to use the bus.
The token bus access control method limits the token holding time of each station to ensure that each station has the opportunity to obtain the right to use the bus and provide priority services during the token cycle. Therefore, the token bus access control method has good real-time performance.
The station that obtains the token has two data transmission methods, namely the non-response data transmission method, and the response data transmission method. When the non-response data transmission method is adopted, the station that obtains the token can immediately send data to the destination station. After the transmission is completed, the communication process is completed;
When the response data transmission method is adopted, the communication is not completed after the station that obtains the token sends the data to the destination station. The entire communication process must be completed after the destination station obtains the token and sends the response frame to the sending station. The latter’s response time is significantly longer than the former, and the real-time performance is reduced.
The floating master station communication method
The floating master station communication mode is also called N: M communication mode, which is suitable for the PLC network of the bus structure. It means that there are M stations on the bus, of which N (N<M) is the master station and the rest are slave stations.
N: M communication mode adopts the access control technology that combines token bus and master-slave bus. First, the N master stations are formed into a logical ring, and the tokens flow in the logical ring one by one, and the bus usage rights are distributed among the N master stations. This is the meaning of the floating master station. The master station that has obtained the right to use the bus then determines which stations to communicate with within its token holding time in accordance with the master-slave method.
A polling table is configured in the master station, which can be polled according to other master station numbers and slave station numbers arranged on the polling table. The master station that obtains the token can arrange the communication task randomly proposed by the user before or after the polling according to the priority.
The master station that has obtained the right to use the bus can communicate with the destination station in a variety of data transmission methods, among which the non-response and no-connection mode is the fastest.
CSMA/CD communication method
The CSMA/CD communication method is a random communication method, which is suitable for PLC networks with a bus structure. Each station on the bus has equal status, and there is no distinction between master and slave. The CSMA/CD access control method is adopted, that is, listen first, then talk, and talk. While listening.
The CSMA/CD access control method cannot guarantee that within a certain period of time, every station on the PLC network can obtain the right to use the bus, so this is an access control method that cannot guarantee real-time performance. However, it adopts a random method, simple method, and pinholes, as long as the bus is free, it will rush to the Internet, and the utilization rate of communication resources is high. Therefore, the CSMA/CD communication method is suitable for the upper production management subnet in the PLC network.
The data transmission mode of CSMA/CD communication mode can be selected from connection, no connection, response, no response, and broadcast communication. It can be selected according to the requirements of communication speed and reliability.
The above are the commonly used communication methods in PLC networks. In addition, there are a small number of PLC networks that use other communication methods, such as token ring communication methods. In addition, in the newly launched PLC network, multiple communication methods are often integrated and configured on a certain level of the subnet, which is also the trend of future technology development.
Besides the 6 Communication Methods of PLC Network article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
What is the difference between WIFI and WLAN?
Summary of 41 Basic Knowledge of LTE
What Is The 5G Network Slicing?
